Role of SST, CORT and ghrelin and its receptors at the endocrine pancreas
- PMID: 23162532
- PMCID: PMC3444847
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2012.00114
Role of SST, CORT and ghrelin and its receptors at the endocrine pancreas
Abstract
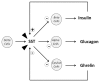
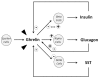
Somatostatin (SST), cortistatin (CORT), and its receptors (sst1-5), and ghrelin and its receptors (GHS-R) are two highly interrelated neuropeptide systems with a broad range of overlapping biological actions at central, cardiovascular, and immune levels among others. Besides their potent regulatory role on GH release, its endocrine actions are highlighted by SST/CORT and ghrelin influence on insulin secretion, glucose homeostasis, and insulin resistance. Interestingly, most components of these systems are expressed at the endocrine pancreas and are actively involved in the modulation of pancreatic islet function and, consequently influence glucose homeostasis. In addition, some of them also participate in islet survival and regeneration. Furthermore, under severe metabolic condition as well as in endocrine pathologies, their expression profile is severely deregulated. These findings suggest that SST/CORT and ghrelin systems could play a relevant role in pancreatic function under metabolic and endocrine pathologies. Accordingly, these systems have been therapeutically targeted for the prevention or amelioration of certain metabolic conditions (obesity) as well as for tumor growth inhibition and/or hormonal regulation in endocrine pathologies (neuroendocrine tumors). This review focuses on the interrelationship between SST/CORT and ghrelin systems and their role in severe metabolic conditions and some endocrine disorders.
Keywords: CORT; SST; endocrine; ghrelin; insulin; islet; pancreas.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of endogenous cortistatin in the regulation of ghrelin system expression at pancreatic level under normal and obese conditions.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57834. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057834. Epub 2013 Feb 28. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23469081 Free PMC article.
-
Not So Giants: Mice Lacking Both Somatostatin and Cortistatin Have High GH Levels but Show No Changes in Growth Rate or IGF-1 Levels.Endocrinology. 2015 Jun;156(6):1958-64. doi: 10.1210/en.2015-1132. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Endocrinology. 2015. PMID: 25830706
-
Cortistatin is not a somatostatin analogue but stimulates prolactin release and inhibits GH and ACTH in a gender-dependent fashion: potential role of ghrelin.Endocrinology. 2011 Dec;152(12):4800-12. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-1542. Epub 2011 Oct 4. Endocrinology. 2011. PMID: 21971153 Free PMC article.
-
Endocrine actions of cortistatin: in vivo studies.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008 May 14;286(1-2):123-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2007.12.012. Epub 2007 Dec 27. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18281148 Review.
-
Ghrelin: endocrine, metabolic and cardiovascular actions.J Endocrinol Invest. 2005;28(5 Suppl):23-5. J Endocrinol Invest. 2005. PMID: 16114271 Review.
Cited by
-
The ameliorative potential of ethanolic extract of propolis on hematotoxicity and structural neuronal damage in hyperthermia-exposed rats.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2016 Aug;19(8):875-882. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27746870 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Cortistatin Level in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Relationship with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Int J Gen Med. 2023 Feb 21;16:631-639. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S396315. eCollection 2023. Int J Gen Med. 2023. PMID: 36851999 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure to cell phone radiofrequency changes corticotrophin hormone levels and histology of the brain and adrenal glands in male Wistar rat.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018 Dec;21(12):1269-1274. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2018.29567.7133. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30627371 Free PMC article.
-
Fermentation quality of herbal tea residue and its application in fattening cattle under heat stress.BMC Vet Res. 2021 Nov 12;17(1):348. doi: 10.1186/s12917-021-03061-y. BMC Vet Res. 2021. PMID: 34772402 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of acute heat stress on adrenocorticotropic hormone, cortisol, interleukin-2, interleukin-12 and apoptosis gene expression in rats.Biomed Rep. 2015 May;3(3):425-429. doi: 10.3892/br.2015.445. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Biomed Rep. 2015. PMID: 26137249 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al Massadi O., Tschop M. H., Tong J. (2011). Ghrelin acylation and metabolic control. Peptides 32 2301–2308 - PubMed
-
- Angelidis G., Valotassiou V., Georgoulias P. (2010). Current and potential roles of ghrelin in clinical practice. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 33 823–838 - PubMed
-
- Asakawa A., Inui A., Kaga T., Yuzuriha H., Nagata T., Fujimiya M., Katsuura G., Makino S., Fujino M. A., Kasuga M. (2001). A role of ghrelin in neuroendocrine and behavioral responses to stress in mice. Neuroendocrinology 74 143–147 - PubMed
-
- Aydin S., Sahin I., Ozkan Y., Dag E., Gunay A., Guzel S. P., Catak Z., Ozercan M. R. (2012). Examination of the tissue ghrelin expression of rats with diet-induced obesity using radioimmunoassay and immunohistochemical methods. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 365 165–173 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

