The role of CTCF binding sites in the 3' immunoglobulin heavy chain regulatory region
- PMID: 23162572
- PMCID: PMC3499808
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2012.00251
The role of CTCF binding sites in the 3' immunoglobulin heavy chain regulatory region
Abstract
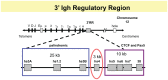
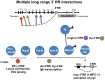
The immunoglobulin heavy chain locus undergoes a series of DNA rearrangements and modifications to achieve the construction and expression of individual antibody heavy chain genes in B cells. These events affect variable regions, through VDJ joining and subsequent somatic hypermutation, and constant regions through class switch recombination (CSR). Levels of IgH expression are also regulated during B cell development, resulting in high levels of secreted antibodies from fully differentiated plasma cells. Regulation of these events has been attributed primarily to two cis-elements that work from long distances on their target sequences, i.e., an ∼1 kb intronic enhancer, Eμ, located between the V region segments and the most 5' constant region gene, Cμ; and an ∼40 kb 3' regulatory region (3' RR) that is located downstream of the most 3' C(H) gene, Cα. The 3' RR is a candidate for an "end" of B cell-specific regulation of the Igh locus. The 3' RR contains several B cell-specific enhancers associated with DNase I hypersensitive sites (hs1-4), which are essential for CSR and for high levels of IgH expression in plasma cells. Downstream of this enhancer-containing region is a region of high-density CTCF binding sites, which extends through hs5, 6, and 7 and further downstream. CTCF, with its enhancer-blocking activities, has been associated with all mammalian insulators and implicated in multiple chromosomal interactions. Here we address the 3' RR CTCF-binding region as a potential insulator of the Igh locus, an independent regulatory element and a predicted modulator of the activity of 3' RR enhancers. Using chromosome conformation capture technology, chromatin immunoprecipitation, and genetic approaches, we have found that the 3' RR with its CTCF-binding region interacts with target sequences in the V(H), Eμ, and C(H) regions through DNA looping as regulated by protein binding. This region impacts on B cell-specific Igh processes at different stages of B cell development.
Keywords: CTCF; Pax5, chromosome conformation capture (3C) assay; class switch recombination; enhancers; immunoglobulin heavy chain gene locus; insulators.
Figures
References
-
- Amouyal M. (2010). Gene insulation. Part II: natural strategies in vertebrates. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 88 885–898 - PubMed
-
- Bebin A. G., Carrion C., Marquet M., Cogne N., Lecardeur S., Cogne M., et al. (2010). In vivo redundant function of the 3′ IgH regulatory element HS3b in the mouse. J. Immunol. 184 3710–3717 - PubMed
-
- Calvo C.-F., Giannini S. L., Martinez N., Birshtein B. K. (1991). DNA sequences 3′ of the IgH chain cluster rearrange in mouse B cell lines. J. Immunol. 146 1353–1360 - PubMed
-
- Chen C., Birshtein B. K. (1996). A region of 20 bp repeats lies 3′ of human Ig Cα1 and Cα2 genes. Int. Immunol. 8 115–122 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

