Neurofibromatosis type I (von Recklinghausen's disease): A family case report and literature review
- PMID: 23162593
- PMCID: PMC3491339
Neurofibromatosis type I (von Recklinghausen's disease): A family case report and literature review
Abstract
The term neurofibromatosis (NF) is used for a group of genetic disorders that primarily affect the cell growth of neural tissues. Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), also known as von Recklinghausen's disease, is the most common type of NF, and accounts for about 90% of all cases. It is one of the most frequent human genetic diseases, with a prevalence of one case in 3,000 births. The expressivity of NF1 is extremely variable, with manifestations ranging from mild lesions to several complications and functional impairment. Oral manifestations can be found in almost 72% of the NF1 patients. The aim of this article is to report the NF1 in a family with different manifestations and to review the literature.
Keywords: Genetic diseases; neurofibromatosis type 1; von Recklinghausen's disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
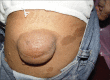
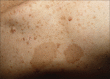
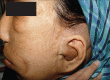
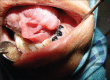
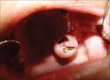
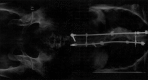
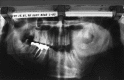
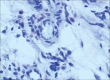
References
-
- Gorlin RJ, Cohen MM, Levin LF. Syndromes of the head and neck. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1990. pp. 353–416.
-
- Friedman JM, Gutmann DH, MacCollin M, Riccardi Y. Phenotype, natural history and pathogenesis. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press; 1999. Neurofibromatosis.
-
- Cunha KS, Barboza EP, Dias EP, Oliveira FM. Neurofibromatosis type I with periodontal manifestation. A case report and literature review. Br Dent J. 2004;196:457–60. - PubMed
-
- Bekisz O, Darimont F, Rompen EH. Diffuse but unilateral gingival enlargement associated with von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis: A case report. J Clin Periodontol. 2000;27:361–5. - PubMed
-
- García-de Marcos JA, Dean-Ferrer A, Alamillos-Granados F, Ruiz- Masera JJ, García-de Marcos MJ, Vidal-Jiménez A, et al. Gingival neurofibroma in a neurofibromatosis type 1 patient. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2007;12:E287–91. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
