A pilot study of extremely low-frequency magnetic fields in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: Effects on survival and palliation of general symptoms
- PMID: 23162666
- PMCID: PMC3499610
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2012.867
A pilot study of extremely low-frequency magnetic fields in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: Effects on survival and palliation of general symptoms
Abstract
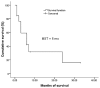
The inhibitory effects of magnetic fields (MFs) on tumor cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo have been reported in previous studies. However, the effects of MFs in the treatment of cancer have not been described in clinical trials. We investigated the effects of 420 r/min, 0.4-T extremely low-frequency MFs (ELF-MFs) on the survival and palliation of general symptoms in 13 advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Toxicity and side-effects were assessed according to WHO criteria. The treatment area included the primary tumor site, metastatic sites and metastatic lymph nodes. Additionally, the patients were treated 2 h per day, 5 days per week for 6-10 weeks. The changes in general symptoms were analyzed during ELF-MF treatment and 2 weeks after the completion of therapy. Results of physical examination, routine analysis of blood, ECG and liver function, biochemical and kidney function tests were evaluated before and following treatment. All 13 patients were followed up by outpatient service or telephone interview. Our results demonstrated that decreased pleural effusion, remission of shortness of breath, relief of cancer pain, increased appetite, improved physical strength, regular bowel movement and better sleep quality was detected in 2 (15.4%), 5 (38.5%), 5 (38.5%), 6 (46.2%), 9 (69.2%), 1 (7.7%) and 2 (15.4%) patients, respectively. However, the palliation of symptoms in 2 (15.4%) patients was observed during therapy and disappeared at treatment termination. No severe toxicity or side-effects were detected in our trial. The median survival was 6.0 months (95% CI, 1.0-11.0). The 1- and 2-year survival rates were 31.7 and 15.9%, respectively. This study is the first to describe survival and palliation of general symptoms in advanced NSCLC patients treated with ELF-MFs. As an effective, well-tolerated and safe treatment choice, ELF-MFs may prolong survival and improve general symptoms of advanced NSCLC patients. However, this treatment strategy requires further research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of low-frequency rotary magnetic fields on advanced gastric cancer: Survival and palliation of general symptoms.J Cancer Res Ther. 2018;14(4):815-819. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_991_17. J Cancer Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29970658
-
Extremely low frequency magnetic fields regulate differentiation of regulatory T cells: Potential role for ROS-mediated inhibition on AKT.Bioelectromagnetics. 2016 Feb;37(2):89-98. doi: 10.1002/bem.21954. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Bioelectromagnetics. 2016. PMID: 26807660
-
The role of 217-Hz ELF magnetic fields emitted from GSM mobile phones on electrochemotherapy mechanisms.Electromagn Biol Med. 2020 Jul 2;39(3):239-249. doi: 10.1080/15368378.2020.1762635. Epub 2020 May 15. Electromagn Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 32410511
-
A consensus panel review of central nervous system effects of the exposure to low-intensity extremely low-frequency magnetic fields.Brain Stimul. 2013 Jul;6(4):469-76. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2013.01.004. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Brain Stimul. 2013. PMID: 23428499 Review.
-
Effects of ZD1839 (Iressa, gefitinib) treatment on symptoms and quality of life in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Semin Oncol. 2004 Jun;31(3 Suppl 9):23-30. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2004.04.010. Semin Oncol. 2004. PMID: 15206079 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential mechanisms and clinical applications of static magnetic field therapy in glioma.Front Neurol. 2025 Jun 25;16:1594874. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1594874. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40635706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spinning magnetic field patterns that cause oncolysis by oxidative stress in glioma cells.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 7;13(1):19264. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46758-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37935811 Free PMC article.
-
Low-frequency magnetic field therapy for glioblastoma: Current advances, mechanisms, challenges and future perspectives.J Adv Res. 2025 Mar;69:531-543. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.03.024. Epub 2024 Mar 31. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 38565404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thermodynamic Considerations on the Biophysical Interaction between Low-Energy Electromagnetic Fields and Biosystems.Membranes (Basel). 2024 Aug 22;14(8):179. doi: 10.3390/membranes14080179. Membranes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39195431 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huang L, Dong L, Chen Y, Qi H, Xiao D. Effects of sinusoidal magnetic field observed on cell proliferation, ion concentration, and osmolarity in two human cancer cell lines. Electromagn Biol Med. 2006;25:113–126. - PubMed
-
- Tofani S, Barone D, Berardelli M, Berno E, Cintorino M, Foglia L, Ossola P, Ronchetto F, Toso E, Eandi M. Static and ELF magnetic fields enhance the in vivo anti-tumor efficacy of cis-platin against lewis lung carcinoma, but not of cyclophosphamide against B16 melanotic melanoma. Pharmacol Res. 2003;48:83–90. - PubMed
-
- Novikov VV, Novikov GV, Fesenko EE. Effect of weak combined static and extremely low-frequency alternating magnetic fields on tumor growth in mice inoculated with the Ehrlich ascites carcinoma. Bioelectromagnetics. 2009;30:343–351. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Zhang H, Zheng C, Li C, Zhang X, Xiong W. Extremely low frequency (ELF) pulsed-gradient magnetic fields inhibit malignant tumour growth at different biological levels. Cell Biol Int. 2002;26:599–603. - PubMed
-
- Ronchetto F, Barone D, Cintorino M, Berardelli M, Lissolo S, Orlassino R, Ossola P, Tofani S. Extremely low frequency-modulated static magnetic fields to treat cancer: A pilot study on patients with advanced neoplasm to assess safety and acute toxicity. Bioelectromagnetics. 2004;25:563–571. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials