An ENU mutagenesis approach to dissect "self"-induced immune responses: Unraveling the genetic footprint of immunosurveillance
- PMID: 23162753
- PMCID: PMC3489741
- DOI: 10.4161/onci.20580
An ENU mutagenesis approach to dissect "self"-induced immune responses: Unraveling the genetic footprint of immunosurveillance
Abstract
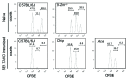
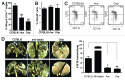
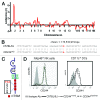
The immune system exerts a critical function as it recognizes and eliminates transformed or neoplastic cells, a process also referred to as immunosurveillance. NK cells play a particularly important role in that they are able to recognize tumor cells via "missing-self"-i.e., the absence of major histocompatibility complex Class I on target cells. Moreover, recent studies suggest that NK cells also participate in the onset and regulation of adaptive immune responses. The exact molecular pathways by which this occurs, however, remain poorly understood. To obtain further insight into the genes that are required for self-induced immune responses via NK cell-mediated cell death, our laboratory initiated a forward genetic approach using N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU) as a mutagen. Specifically, we tested the ability of NK cells from G3 ENU germline mice to recognize missing-self target cells and induce CD8+ T-cell responses following immunization with irradiated tumor cells. Here we present two ENU germline mutants, designated Ace and Chip, that are defective in the recognition of β-2 microglobulin-deficient target cells, yet exhibit improved clearance of B16 melanoma cells in vivo. Coarse mapping and whole genome sequencing of the Chip mutation revealed a missense mutation causing a T'A amino acid substitution in the highly conserved third immuno-receptor tyrosine-based switch motif of CD244 (2B4). The forward genetic approach described here promises to reveal important insight into critical genes that are required for host responses involved in anticancer immunity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Slp-76 is a critical determinant of NK-cell mediated recognition of missing-self targets.Eur J Immunol. 2015 Jul;45(7):2072-83. doi: 10.1002/eji.201445352. Epub 2015 May 22. Eur J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25929249 Free PMC article.
-
2B4 (CD244)-CD48 interactions provide a novel MHC class I-independent system for NK-cell self-tolerance in mice.Blood. 2005 Aug 15;106(4):1337-40. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-01-0357. Epub 2005 May 3. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15870174 Free PMC article.
-
Natural killer cells play a role in MHC class I in vivo induction in tumor cells that are MHC negative in vitro.Int J Oncol. 2005 Mar;26(3):679-84. Int J Oncol. 2005. PMID: 15703823
-
A review of the genotoxicity of 1-ethyl-1-nitrosourea.Mutat Res. 1993 Jul;297(1):3-38. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(93)90005-8. Mutat Res. 1993. PMID: 7686271 Review.
-
Teleost T and NK cell immunity.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013 Aug;35(2):197-206. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2013.04.018. Epub 2013 May 7. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23664867 Review.
Cited by
-
Gab3 is required for IL-2- and IL-15-induced NK cell expansion and limits trophoblast invasion during pregnancy.Sci Immunol. 2019 Aug 2;4(38):eaav3866. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aav3866. Sci Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31375526 Free PMC article.
-
Central role of gimap5 in maintaining peripheral tolerance and T cell homeostasis in the gut.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:436017. doi: 10.1155/2015/436017. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 25944983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD244 represents a new therapeutic target in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.J Immunother Cancer. 2020 Mar;8(1):e000245. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2019-000245. J Immunother Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32217758 Free PMC article.
-
Slp-76 is a critical determinant of NK-cell mediated recognition of missing-self targets.Eur J Immunol. 2015 Jul;45(7):2072-83. doi: 10.1002/eji.201445352. Epub 2015 May 22. Eur J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25929249 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
