Meaningful family relationships: neurocognitive buffers of adolescent risk taking
- PMID: 23163412
- PMCID: PMC3932333
- DOI: 10.1162/jocn_a_00331
Meaningful family relationships: neurocognitive buffers of adolescent risk taking
Abstract
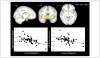
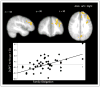
Discordant development of brain regions responsible for cognitive control and reward processing may render adolescents susceptible to risk taking. Identifying ways to reduce this neural imbalance during adolescence can have important implications for risk taking and associated health outcomes. Accordingly, we sought to examine how a key family relationship-family obligation-can reduce this vulnerability. Forty-eight adolescents underwent an fMRI scan during which they completed a risk-taking and cognitive control task. Results suggest that adolescents with greater family obligation values show decreased activation in the ventral striatum when receiving monetary rewards and increased dorsolateral PFC activation during behavioral inhibition. Reduced ventral striatum activation correlated with less real-life risk-taking behavior and enhanced dorsolateral PFC activation correlated with better decision-making skills. Thus, family obligation may decrease reward sensitivity and enhance cognitive control, thereby reducing risk-taking behaviors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Longitudinal Changes in Prefrontal Cortex Activation Underlie Declines in Adolescent Risk Taking.J Neurosci. 2015 Aug 12;35(32):11308-14. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1553-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26269638 Free PMC article.
-
Adolescent risky decision-making: neurocognitive development of reward and control regions.Neuroimage. 2010 May 15;51(1):345-55. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.02.038. Epub 2010 Feb 24. Neuroimage. 2010. PMID: 20188198
-
Neural activation during delay discounting is associated with 6-month change in risky sexual behavior in adolescents.Ann Behav Med. 2018 Apr 19;52(5):356-366. doi: 10.1093/abm/kax028. Ann Behav Med. 2018. PMID: 29684133 Free PMC article.
-
[Risk-taking in adolescence: A neuroeconomics approach].Encephale. 2010 Apr;36(2):147-54. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2009.06.004. Epub 2009 Sep 22. Encephale. 2010. PMID: 20434632 Review. French.
-
Meta-analysis and review of functional neuroimaging differences underlying adolescent vulnerability to substance use.Neuroimage. 2020 Apr 1;209:116476. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.116476. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Neuroimage. 2020. PMID: 31875520 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Decreased modulation by the risk level on the brain activation during decision making in adolescents with internet gaming disorder.Front Behav Neurosci. 2015 Nov 3;9:296. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2015.00296. eCollection 2015. Front Behav Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26578922 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting risk decisions in a modified Balloon Analogue Risk Task: Conventional and single-trial ERP analyses.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2018 Feb;18(1):99-116. doi: 10.3758/s13415-017-0555-3. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29204798
-
Family obligation moderates longitudinal associations between parental psychological control and adjustment of urban adolescents.Int J Behav Dev. 2024 Sep;48(5):411-421. doi: 10.1177/01650254241233532. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Int J Behav Dev. 2024. PMID: 39184345 Free PMC article.
-
Do Hostile School Environments Promote Social Deviance by Shaping Neural Responses to Social Exclusion?J Res Adolesc. 2018 Mar;28(1):103-120. doi: 10.1111/jora.12340. J Res Adolesc. 2018. PMID: 29460355 Free PMC article.
-
Moderate social sensitivity in a risky context supports adaptive decision making in adolescence: evidence from brain and behavior.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2018 May 1;13(5):546-556. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsy016. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29529318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander CS, Kim YJ, Ensminger M, Johnson KE, Smith BJ, Dolan LJ. A measure of risk taking for young adolescents: Reliability and validity assessments. Journal of Youth and Adolescence. 1990;19:559–569. - PubMed
-
- Armsden GC, Greenberg MT. The inventory of parent and peer attachment: Individual differences and their relationship to psychological well-being in adolescence. Journal of Youth and Adolescence. 1987;16:427–445. - PubMed
-
- Arnett JJ. Reckless behavior in adolescence: A developmental perspective. Developmental Review. 1992;12:339–373.
-
- Beckmann C, Jenkinson M, Smith S. General multilevel linear modeling for group analysis in fMRI. Neuroimage. 2003;20:1052–1063. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

