Cu(II)-catalyzed aerobic hydroperoxidation of Meldrum's acid derivatives and application in intramolecular oxidation: a conceptual blueprint for O2/H2 dihydroxylation
- PMID: 23163733
- PMCID: PMC3518688
- DOI: 10.1021/ol302848m
Cu(II)-catalyzed aerobic hydroperoxidation of Meldrum's acid derivatives and application in intramolecular oxidation: a conceptual blueprint for O2/H2 dihydroxylation
Abstract
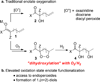
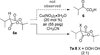
Aerobic hydroperoxidation of Meldrum's acid derivatives via a Cu(II)-catalyzed process is presented. The mild reaction conditions are tolerant to pendant unsaturation allowing the formation of endoperoxides via electrophilic activation. Cleavage of the O-O bond provides 1,n-diols with differentiation of the hydroxy groups.
Figures



References
-
- Smith AMR, Hii KK. Chem. Rev. 2011;111:1637–1656. - PubMed
-
-
Chen B-C, Zhou P, Davis FA, Ciganek E. Org. React. (N.Y.) 2003;62:1–356. (b) For direct hydroxylation of active methines using Pd(II)/O2 see: Chuang GJ, Wang W, Lee E, Ritter T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011;133:1760–1762.
-
-
- Burns NZ, Baran PS, Hoffmann RW. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009;48:2854–2867. - PubMed
-
-
For recent reviews of Meldrum’s acid in organic synthesis: Dumas AM, Fillion E. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010;43:440–454. Ivanov AS. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008;37:789–811.
-
-
- Keiser J, Utzinger J. Curr. Opin. Infect. Diseases. 2007;20:605–612. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

