2D NMR-based metabolomics uncovers interactions between conserved biochemical pathways in the model organism Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 23163760
- PMCID: PMC3574178
- DOI: 10.1021/cb3004644
2D NMR-based metabolomics uncovers interactions between conserved biochemical pathways in the model organism Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
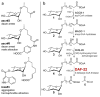
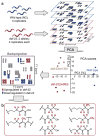
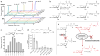
Ascarosides are small-molecule signals that play a central role in C. elegans biology, including dauer formation, aging, and social behaviors, but many aspects of their biosynthesis remain unknown. Using automated 2D NMR-based comparative metabolomics, we identified ascaroside ethanolamides as shunt metabolites in C. elegans mutants of daf-22, a gene with homology to mammalian 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolases predicted to function in conserved peroxisomal lipid β-oxidation. Two groups of ethanolamides feature β-keto functionalization confirming the predicted role of daf-22 in ascaroside biosynthesis, whereas α-methyl substitution points to unexpected inclusion of methylmalonate at a late stage in the biosynthesis of long-chain fatty acids in C. elegans. We show that ascaroside ethanolamide formation in response to defects in daf-22 and other peroxisomal genes is associated with severe depletion of endocannabinoid pools. These results indicate unexpected interaction between peroxisomal lipid β-oxidation and the biosynthesis of endocannabinoids, which are major regulators of lifespan in C. elegans. Our study demonstrates the utility of unbiased comparative metabolomics for investigating biochemical networks in metazoans.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An acyl-CoA thioesterase is essential for the biosynthesis of a key dauer pheromone in C. elegans.Cell Chem Biol. 2024 May 16;31(5):1011-1022.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.12.006. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Cell Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 38183989 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative metabolomics reveals biogenesis of ascarosides, a modular library of small-molecule signals in C. elegans.J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Jan 25;134(3):1817-24. doi: 10.1021/ja210202y. Epub 2012 Jan 12. J Am Chem Soc. 2012. PMID: 22239548 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Conservation and Divergence of daf-22 Paralogs in Pristionchus pacificus Dauer Development.Mol Biol Evol. 2016 Oct;33(10):2506-14. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw090. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Mol Biol Evol. 2016. PMID: 27189572 Free PMC article.
-
Ascaroside signaling in C. elegans.WormBook. 2013 Jan 18:1-22. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.155.1. WormBook. 2013. PMID: 23355522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ascaroside Pheromones: Chemical Biology and Pleiotropic Neuronal Functions.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 9;20(16):3898. doi: 10.3390/ijms20163898. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31405082 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolomic "Dark Matter" Dependent on Peroxisomal β-Oxidation in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Am Chem Soc. 2018 Feb 28;140(8):2841-2852. doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b11811. Epub 2018 Feb 16. J Am Chem Soc. 2018. PMID: 29401383 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Metabolomics Identifies the Roles of Acyl-CoA Oxidases in the Biosynthesis of Ascarosides and a Complex Family of Secreted N-Acylethanolamines.ACS Chem Biol. 2025 Jun 20;20(6):1298-1308. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.5c00126. Epub 2025 Jun 5. ACS Chem Biol. 2025. PMID: 40468644
-
Modular assembly of primary metabolic building blocks: a chemical language in C. elegans.Chem Biol. 2015 Jan 22;22(1):7-16. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2014.10.012. Epub 2014 Dec 4. Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25484238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reducing Mass Confusion over the Microbiome.Anal Chem. 2023 Nov 21;95(46):16775-16785. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c02408. Epub 2023 Nov 7. Anal Chem. 2023. PMID: 37934885 Free PMC article.
-
An acyl-CoA thioesterase is essential for the biosynthesis of a key dauer pheromone in C. elegans.Cell Chem Biol. 2024 May 16;31(5):1011-1022.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.12.006. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Cell Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 38183989 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kenyon CJ. The genetics of ageing. Nature. 2010;464:504–512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

