Transcription factor complex AP-1 mediates inflammation initiated by Chlamydia pneumoniae infection
- PMID: 23163821
- PMCID: PMC3593943
- DOI: 10.1111/cmi.12071
Transcription factor complex AP-1 mediates inflammation initiated by Chlamydia pneumoniae infection
Abstract
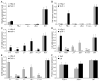
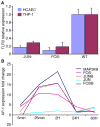
Chlamydia pneumoniae is responsible for a high prevalence of respiratory infections worldwide and has been implicated in atherosclerosis. Inflammation is regulated by transcription factor (TF) networks. Yet, the core TF network triggered by chlamydiae remains largely unknown. Primary human coronary artery endothelial cells were mock-infected or infected with C. pneumoniae to generate human transcriptome data throughout the chlamydial developmental cycle. Using systems network analysis, the predominant TF network involved receptor, binding and adhesion and immune response complexes. Cells transfected with interfering RNA against activator protein-1 (AP-1) members FOS, FOSB, JUN and JUNB had significantly decreased expression and protein levels of inflammatory mediators interleukin (IL)6, IL8, CD38 and tumour necrosis factor compared with controls. These mediators have been shown to be associated with C. pneumoniae disease. Expression of AP-1 components was regulated by MAPK3K8, a MAPK pathway component. Additionally, knock-down of JUN and FOS showed significantly decreased expression of Toll-like receptor (TLR)3 during infection, implicating JUN and FOS in TLR3 regulation. TLR3 stimulation led to elevated IL8. These findings suggest that C. pneumoniae initiates signalling via TLR3 and MAPK that activate AP-1, a known immune activator in other bacteria not previously shown for chlamydiae, triggering inflammation linked to C. pneumoniae disease.
© 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
AP-1 Transcription Factor Serves as a Molecular Switch between Chlamydia pneumoniae Replication and Persistence.Infect Immun. 2015 Jul;83(7):2651-60. doi: 10.1128/IAI.03083-14. Epub 2015 Apr 20. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 25895972 Free PMC article.
-
Purinergic P2Y2 Receptor Control of Tissue Factor Transcription in Human Coronary Artery Endothelial Cells: NEW AP-1 TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR SITE AND NEGATIVE REGULATOR.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jan 22;291(4):1553-1563. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.681163. Epub 2015 Dec 2. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26631725 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in cell activation by Chlamydophila pneumoniae and Chlamydia trachomatis infection in human endothelial cells.Infect Immun. 2004 Nov;72(11):6615-21. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.11.6615-6621.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15501794 Free PMC article.
-
Pivotal Pathogenic and Biomarker Role of Chlamydia Pneumoniae in Neurovascular Diseases.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2018;15(3):262-273. doi: 10.2174/1567202615666180717161807. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2018. PMID: 30019645 Review.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
Cited by
-
Chlamydia pneumoniae and oxidative stress in cardiovascular disease: state of the art and prevention strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Dec 30;16(1):724-35. doi: 10.3390/ijms16010724. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25561227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytobiotics to improve health and production of broiler chickens: functions beyond the antioxidant activity.Anim Biosci. 2021 Mar;34(3):345-353. doi: 10.5713/ab.20.0842. Epub 2021 Feb 14. Anim Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33705621 Free PMC article.
-
Systematically dissecting the global mechanism of miRNA functions in mouse pluripotent stem cells.BMC Genomics. 2015 Jul 1;16(1):490. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1706-y. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26126859 Free PMC article.
-
DNA or Protein Methylation-Dependent Regulation of Activator Protein-1 Function.Cells. 2021 Feb 21;10(2):461. doi: 10.3390/cells10020461. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33670008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temporal dynamics of the bat wing transcriptome: Insight into gene-expression changes that enable protection against pathogen.Virulence. 2023 Dec;14(1):2156185. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2022.2156185. Virulence. 2023. PMID: 36599840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balasubramanian A, Ganju RK, Groopman JE. Hepatitis C virus and HIV envelope proteins collaboratively mediate interleukin-8 secretion through activation of p38 MAP kinase and SHP2 in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:35755–35766. - PubMed
-
- Belland RJ, Ouellette SP, Gieffers J, Byrne GI. Chlamydia pneumoniae and atherosclerosis. Cell Microbiol. 2004;6:117–127. - PubMed
-
- Betts HJ, Wolf K, Fields KA. Effector protein modulation of host cells: examples in the Chlamydia spp. arsenal. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2009;12:81–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

