Sustaining rapid vesicular release at active zones: potential roles for vesicle tethering
- PMID: 23164531
- PMCID: PMC4748400
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tins.2012.10.001
Sustaining rapid vesicular release at active zones: potential roles for vesicle tethering
Abstract
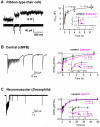
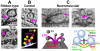
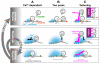
Rapid information processing in our nervous system relies on high-frequency fusion of transmitter-filled vesicles at chemical synapses. Some sensory synapses possess prominent electron-dense ribbon structures that provide a scaffold for tethering synaptic vesicles at the active zone (AZ), enabling sustained vesicular release. Here, we review functional data indicating that some central and neuromuscular synapses can also sustain vesicle-fusion rates that are comparable to those of ribbon-type sensory synapses. Comparison of the ultrastructure across these different types of synapses, together with recent work showing that cytomatrix proteins can tether vesicles and speed vesicle reloading, suggests that filamentous structures may play a key role in vesicle supply. We discuss potential mechanisms by which vesicle tethering could contribute to sustained high rates of vesicle fusion across ribbon-type, central, and neuromuscular synapses.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Katz B. The Release of Neural Transmitter Substances. Liverpool University Press; 1969.
-
- de Ruyter van Steveninck RR, Laughlin SB. The rate of information transfer at graded-potential synpases. Nature. 1996;379:642–645.
-
- Pangršič T, et al. Hearing requires otoferlin-dependent efficient replenishment of synaptic vesicles in hair cells. Nat. Neurosci. 2010;13:869–876. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

