Nuclear factor-κB in pancreatitis: Jack-of-all-trades, but which one is more important?
- PMID: 23164573
- PMCID: PMC6663071
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.11.016
Nuclear factor-κB in pancreatitis: Jack-of-all-trades, but which one is more important?
Abstract
See “Deletion of IκBα activates RelA to reduce acute pancreatitis in mice through up-regulation of Spi2A,” by Neuhöfer P, Liang S, Einwächter H, et al, on page 192; and “Activation of nuclear factor-κB in acinar cells increases the severity of pancreatitis in mice,” by Huang H, Liu Y, Daniluk J, et al, on page 202.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
The authors disclose no conflicts.
Figures
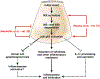
Comment on
-
Activation of nuclear factor-κB in acinar cells increases the severity of pancreatitis in mice.Gastroenterology. 2013 Jan;144(1):202-10. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.09.059. Epub 2012 Oct 3. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23041324 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of IκBα activates RelA to reduce acute pancreatitis in mice through up-regulation of Spi2A.Gastroenterology. 2013 Jan;144(1):192-201. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.09.058. Epub 2012 Oct 3. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23041330
References
-
- Perkins ND. Integrating cell-signalling pathways with NF-kappaB and IKK function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007;8:49–62. - PubMed
-
- Chariot A. The NF-kappaB-independent functions of IKK subunits in immunity and cancer. Trends Cell Biol 2009;19:404–413. - PubMed
-
- Hinz M, Arslan SÇ, Scheidereit C. It takes two to tango: IκBs, the multifunctional partners of NF-κB. Immunol Rev 2012;246: 59–76. - PubMed
-
- Smale ST. Dimer-specific regulatory mechanisms within the NF-κB family of transcription factors. Immunol Rev 2012;246:193–204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

