Synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus shows resistance to acute ethanol exposure in transgenic mice with astrocyte-targeted enhanced CCL2 expression
- PMID: 23164616
- PMCID: PMC3595200
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.11.007
Synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus shows resistance to acute ethanol exposure in transgenic mice with astrocyte-targeted enhanced CCL2 expression
Abstract
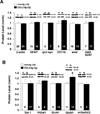
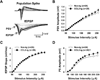
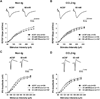
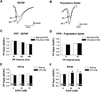
It has been shown that ethanol exposure can activate astrocytes and microglia resulting in the production of neuroimmune factors, including the chemokine CCL2. The role of these neuroimmune factors in the effects of ethanol on the central nervous system has yet to be elucidated. To address this question, we investigated the effects of ethanol on synaptic transmission and plasticity in the hippocampus from mice that express elevated levels of CCL2 in the brain and their non-transgenic littermate controls. The brains of the transgenic mice simulate one aspect of the alcoholic brain, chronically increased levels of CCL2. We used extracellular field potential recordings in acutely isolated hippocampal slices to identify neuroadaptive changes produced by elevated levels of CCL2 and how these neuroadaptive changes affect the actions of acute ethanol. Results showed that synaptic transmission and the effects of ethanol on synaptic transmission were similar in the CCL2-transgenic and non-transgenic hippocampus. However, long-term potentiation (LTP), a cellular mechanism thought to underlie learning and memory, in the CCL2-transgenic hippocampus was resistant to the ethanol-induced depression of LTP observed in the non-transgenic hippocampus. Consistent with these results, ethanol pretreatment significantly impaired cued and contextual fear conditioning in non-transgenic mice, but had no effect in CCL2-transgenic mice. These data show that chronically elevated levels of CCL2 in the hippocampus produce neuroadaptive changes that block the depressing effects of ethanol on hippocampal synaptic plasticity and support the hypothesis that CCL2 may provide a neuroprotective effect against the devastating actions of ethanol on hippocampal function.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

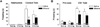

Similar articles
-
Altered hippocampal synaptic function in transgenic mice with increased astrocyte expression of CCL2 after withdrawal from chronic alcohol.Neuropharmacology. 2018 Jun;135:113-125. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.02.031. Epub 2018 Feb 27. Neuropharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29499275 Free PMC article.
-
Altered hippocampal synaptic transmission in transgenic mice with astrocyte-targeted enhanced CCL2 expression.Brain Behav Immun. 2011 Jun;25 Suppl 1(0 1):S106-19. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2011.02.013. Epub 2011 Feb 26. Brain Behav Immun. 2011. PMID: 21356306 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic mice with increased astrocyte expression of IL-6 show altered effects of acute ethanol on synaptic function.Neuropharmacology. 2016 Apr;103:27-43. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.12.015. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Neuropharmacology. 2016. PMID: 26707655 Free PMC article.
-
Acute and chronic effects of ethanol on learning-related synaptic plasticity.Alcohol. 2014 Feb;48(1):1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2013.09.045. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Alcohol. 2014. PMID: 24447472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Instructive roles of astrocytes in hippocampal synaptic plasticity: neuronal activity-dependent regulatory mechanisms.FEBS J. 2022 Apr;289(8):2202-2218. doi: 10.1111/febs.15878. Epub 2021 May 10. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 33864430 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glial gene networks associated with alcohol dependence.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 29;9(1):10949. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-47454-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31358844 Free PMC article.
-
Glial mechanisms underlying substance use disorders.Eur J Neurosci. 2019 Aug;50(3):2574-2589. doi: 10.1111/ejn.14163. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Eur J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30240518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethanol and Cytokines in the Central Nervous System.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2018;248:397-431. doi: 10.1007/164_2017_77. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29236160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of ethanol on immune response in the brain: region-specific changes in adolescent versus adult mice.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014 Feb;38(2):384-91. doi: 10.1111/acer.12244. Epub 2013 Aug 22. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014. PMID: 24033454 Free PMC article.
-
Altered hippocampal synaptic function in transgenic mice with increased astrocyte expression of CCL2 after withdrawal from chronic alcohol.Neuropharmacology. 2018 Jun;135:113-125. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.02.031. Epub 2018 Feb 27. Neuropharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29499275 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allgaier C. Ethanol sensitivity of NMDA receptors. Neurochem. Int. 2002;41:377–382. - PubMed
-
- Ambrosini E, Aloisi F. Chemokines and glial cells: a complex network in the central nervous system. Neurochem. Res. 2004;29:1017–1038. - PubMed
-
- Bertollini C, Ragozzino D, Gross C, Limatola C, Eusebi F. Fractalkine/CX3CL1 depresses central synaptic transmission in mouse hippocampal slices. Neuropharmacology. 2006;51:816–821. - PubMed
-
- Blitzer RD, Gil O, Landau EM. Long-term potentiation in rat hippocampus is inhibited by low concentrations of ethanol. Brain Res. 1990;537:203–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

