Functional in vivo delivery of multiplexed anti-HIV-1 siRNAs via a chemically synthesized aptamer with a sticky bridge
- PMID: 23164935
- PMCID: PMC3538316
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2012.226
Functional in vivo delivery of multiplexed anti-HIV-1 siRNAs via a chemically synthesized aptamer with a sticky bridge
Abstract
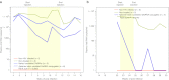
One of the most formidable impediments to clinical translation of RNA interference (RNAi) is safe and effective delivery of the siRNAs to the desired target tissue at therapeutic doses. We previously described in vivo cell type-specific delivery of anti-HIV small-interfering RNAs (siRNAs) through covalent conjugation to an anti-gp120 aptamer. In order to improve the utility of aptamers as siRNA delivery vehicles, we chemically synthesized the gp120 aptamer with a 3' 7-carbon linker (7C3), which in turn is attached to a 16-nucleotide 2' OMe/2' Fl GC-rich bridge sequence. This bridge facilitates the noncovalent binding and interchange of various siRNAs with the same aptamer. We show here that this aptamer-bridge-construct complexed with three different Dicer substrate siRNAs (DsiRNAs) results in effective delivery of the cocktail of DsiRNAs in vivo, resulting in knockdown of target mRNAs and potent inhibition of HIV-1 replication. Following cessation of the aptamer-siRNA cocktail treatment, HIV levels rebounded facilitating a follow-up treatment with the aptamer cocktail of DsiRNAs. This follow-up injection resulted in complete suppression of HIV-1 viral loads that extended several weeks beyond the final injection. Collectively, these data demonstrate a facile, targeted approach for combinatorial delivery of antiviral and host DsiRNAs for HIV-1 therapy in vivo.
Figures




References
-
- Richman DD, Margolis DM, Delaney M, Greene WC, Hazuda D., and, Pomerantz RJ. The challenge of finding a cure for HIV infection. Science. 2009;323:1304–1307. - PubMed
-
- Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE., and, Mello CC. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. - PubMed
-
- Zamore PD, Tuschl T, Sharp PA., and, Bartel DP. RNAi: double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 nucleotide intervals. Cell. 2000;101:25–33. - PubMed
-
- Rossi JJ. RNAi as a treatment for HIV-1 infection. BioTechniques. 2006. pp. 25–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI073255/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL074704/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI096111/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI29329/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI054907/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI042552/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI029329/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI073255/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI42552/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI057066/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI029329/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL07470/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

