Insect microRNAs: biogenesis, expression profiling and biological functions
- PMID: 23165178
- PMCID: PMC3534889
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2012.10.009
Insect microRNAs: biogenesis, expression profiling and biological functions
Abstract
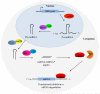
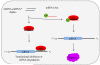
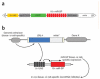
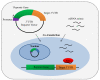
MicroRNAs (miRNA) are a class of endogenous regulatory RNA molecules 21-24 nucleotides in length that modulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level via base pairing to target sites within messenger RNAs (mRNA). Typically, the miRNA "seed sequence" (nucleotides 2-8 at the 5' end) binds complementary seed match sites within the 3' untranslated region of mRNAs, resulting in either translational inhibition or mRNA degradation. MicroRNAs were first discovered in Caenorhabditis elegans and were shown to be involved in the timed regulation of developmental events. Since their discovery in the 1990s, thousands of potential miRNAs have since been identified in various organisms through small RNA cloning methods and/or computational prediction, and have been shown to play functionally important roles of gene regulation in invertebrates, vertebrates, plants, fungi and viruses. Numerous functions of miRNAs identified in Drosophila melanogaster have demonstrated a great significance of these regulatory molecules. However, elucidation of miRNA roles in non-drosophilid insects presents a challenging and important task.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Complementarity to an miRNA seed region is sufficient to induce moderate repression of a target transcript in the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Plant J. 2013 Dec;76(6):1045-56. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12354. Plant J. 2013. PMID: 24127635
-
microRNA expression in the eyes and their significance in relation to functions.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2009 Mar;28(2):87-116. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2008.11.003. Epub 2008 Nov 28. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2009. PMID: 19071227 Review.
-
Computational analysis of microRNA targets in Caenorhabditis elegans.Gene. 2006 Jan 3;365:2-10. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.09.035. Epub 2005 Dec 13. Gene. 2006. PMID: 16356665
-
SmD1 Modulates the miRNA Pathway Independently of Its Pre-mRNA Splicing Function.PLoS Genet. 2015 Aug 26;11(8):e1005475. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005475. eCollection 2015 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26308709 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-Kingdom Regulation of Plant-Derived miRNAs in Modulating Insect Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 28;24(9):7978. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097978. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175684 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pyrethroid-resistance is modulated by miR-92a by targeting CpCPR4 in Culex pipiens pallens.Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 Jan;203:20-24. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Sep 11. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27627779 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral responses of arthropod vectors: an update on recent advances.Virusdisease. 2014;25(3):249-60. doi: 10.1007/s13337-014-0217-9. Epub 2014 Aug 5. Virusdisease. 2014. PMID: 25674592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
microRNA maintains nutrient homeostasis in the symbiont-host interaction.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Sep 3;121(36):e2406925121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2406925121. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39196627 Free PMC article.
-
Anopheles gambiae blood feeding initiates an anticipatory defense response to Plasmodium berghei.J Innate Immun. 2015;7(1):74-86. doi: 10.1159/000365331. Epub 2014 Sep 19. J Innate Immun. 2015. PMID: 25247883 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Screening to Predict MicroRNA Targets in the Flavivirus 3' UTR Genome: An Approach for Antiviral Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 21;25(18):10135. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810135. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337625 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Behm-Ansmant I, Rehwinkel J, Izaurralde E. MicroRNAs silence gene expression by repressing protein expression and/or promoting mRNA decay. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:523–530. - PubMed
-
- Bellés X. Beyond Drosophila: RNAi in vivo and functional genomics in insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010;55:111–128. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM, Hannon GJ. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature. 2001;409:363–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

