Anthelmintic avermectins kill Mycobacterium tuberculosis, including multidrug-resistant clinical strains
- PMID: 23165468
- PMCID: PMC3553693
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01696-12
Anthelmintic avermectins kill Mycobacterium tuberculosis, including multidrug-resistant clinical strains
Abstract
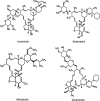
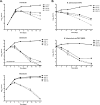
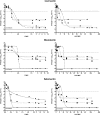
Avermectins are a family of macrolides known for their anthelmintic activities and traditionally believed to be inactive against all bacteria. Here we report that members of the family, ivermectin, selamectin, and moxidectin, are bactericidal against mycobacterial species, including multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant clinical strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Avermectins are approved for clinical and veterinary uses and have documented pharmacokinetic and safety profiles. We suggest that avermectins could be repurposed for tuberculosis treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Payne DJ, Gwynn MN, Holmes DJ, Pompliano DL. 2007. Drugs for bad bugs: confronting the challenges of antibacterial discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 6:29–40 - PubMed
-
- Koul A, Arnoult E, Lounis N, Guillemont J, Andries K. 2011. The challenge of new drug discovery for tuberculosis. Nature 469:483–490 - PubMed
-
- Chong CR, Sullivan DJ., Jr 2007. New uses for old drugs. Nature 448:645–646 - PubMed
-
- Omura S, Crump A. 2004. The life and times of ivermectin—a success story. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2:984–989 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

