Targeted nanoparticle delivery overcomes off-target immunostimulatory effects of oligonucleotides and improves therapeutic efficacy in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 23165478
- PMCID: PMC3538326
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-01-407742
Targeted nanoparticle delivery overcomes off-target immunostimulatory effects of oligonucleotides and improves therapeutic efficacy in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Abstract
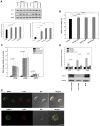
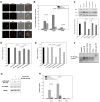
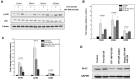
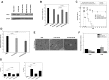
Several RNA-targeted therapeutics, including antisense oligonucleotides (ONs), small interfering RNAs, and miRNAs, constitute immunostimulatory CpG motifs as an integral part of their design. The limited success with free antisense ONs in hematologic malignancies in recent clinical trials has been attributed to the CpG motif-mediated, TLR-induced prosurvival effects and inefficient target modulation in desired cells. In an attempt to diminish their off-target prosurvival and proinflammatory effects and specific delivery, as a proof of principle, in the present study, we developed an Ab-targeted liposomal delivery strategy using a clinically relevant CD20 Ab (rituximab)-conjugated lipopolyplex nanoparticle (RIT-INP)- and Bcl-2-targeted antisense G3139 as archetypical antisense therapeutics. The adverse immunostimulatory responses were abrogated by selective B cell-targeted delivery and early endosomal compartmentalization of G3139-encapsulated RIT-INPs, resulting in reduced NF-κB activation, robust Bcl-2 down-regulation, and enhanced sensitivity to fludarabine-induced cytotoxicity. Furthermore, significant in vivo therapeutic efficacy was noted after RIT-INP-G3139 administration in a disseminated xenograft leukemia model. The results of the present study demonstrate that CD20-targeted delivery overcomes the immunostimulatory properties of CpG-containing ON therapeutics and improves efficient gene silencing and in vivo therapeutic efficacy for B-cell malignancies. The broader implications of similar approaches in overcoming immunostimulatory properties of RNA-directed therapeutics in hematologic malignancies are also discussed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular and pharmacokinetic properties associated with the therapeutics of bcl-2 antisense oligonucleotide G3139 combined with free and liposomal doxorubicin.Clin Cancer Res. 2000 Jul;6(7):2891-902. Clin Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10914739
-
G3139 and other CpG-containing immunostimulatory phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides are potent suppressors of the growth of human tumor xenografts in nude mice.Oligonucleotides. 2006 Spring;16(1):83-93. doi: 10.1089/oli.2006.16.83. Oligonucleotides. 2006. PMID: 16584297
-
Bcl-2 antisense (G3139, Genasense) enhances the in vitro and in vivo response of Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative disease to rituximab.Clin Cancer Res. 2003 May;9(5):1931-9. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12738752
-
Oblimersen sodium (G3139 Bcl-2 antisense oligonucleotide) therapy in Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia: a targeted approach to enhance apoptosis.Semin Oncol. 2003 Apr;30(2):300-4. doi: 10.1053/sonc.2003.50041. Semin Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12720157 Review.
-
Potential therapeutic applications of oblimersen in CLL.Oncology (Williston Park). 2004 Nov;18(13 Suppl 10):32-8. Oncology (Williston Park). 2004. PMID: 15651175 Review.
Cited by
-
A microfluidic method to synthesize transferrin-lipid nanoparticles loaded with siRNA LOR-1284 for therapy of acute myeloid leukemia.Nanoscale. 2014 Aug 21;6(16):9742-51. doi: 10.1039/c4nr01510j. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Nanoscale. 2014. PMID: 25003978 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomedicine and drug delivery strategies for treatment of inflammatory bowel disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Oct 28;21(40):11343-52. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i40.11343. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26525603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pre-clinical immunotoxicity studies of nanotechnology-formulated drugs: Challenges, considerations and strategy.J Control Release. 2015 Dec 28;220(Pt B):571-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.08.056. Epub 2015 Sep 5. J Control Release. 2015. PMID: 26348388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative analysis of metallic nanoparticles as exogenous soft tissue contrast for live in vivo micro-computed tomography imaging of avian embryonic morphogenesis.Dev Dyn. 2016 Oct;245(10):1001-10. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.24433. Epub 2016 Aug 18. Dev Dyn. 2016. PMID: 27447729 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomedicines for cancer therapy: state-of-the-art and limitations to pre-clinical studies that hinder future developments.Front Chem. 2014 Aug 25;2:69. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2014.00069. eCollection 2014. Front Chem. 2014. PMID: 25202689 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Youle RJ, Strasser A. The BCL-2 protein family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9(1):47–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

