Competitive formation of both long-range 5'-5' and short-range antiparallel 3'-3' DNA interstrand cross-links by a trinuclear platinum complex on binding to a 10-mer duplex
- PMID: 23165925
- PMCID: PMC4004642
- DOI: 10.1039/c2dt32079g
Competitive formation of both long-range 5'-5' and short-range antiparallel 3'-3' DNA interstrand cross-links by a trinuclear platinum complex on binding to a 10-mer duplex
Abstract
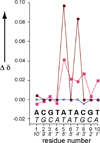
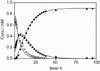
2D [(1)H, (15)N] HSQC NMR spectroscopy has been used to monitor the reaction of fully (15)N-labelled [{trans-PtCl(NH(3))(2)}(2)(μ-trans-Pt(NH(3))(2){NH(2)(CH(2))(6)NH(2)}(2))](4+) (Triplatin, BBR3464 or 1,0,1/t,t,t ((15)N-1)) with the self-complementary 10-mer DNA duplex 5'-{d(ACGTATACGT)(2)} (duplex I) at pH 5.4 and 298 K. Initial electrostatic interactions were observed in the minor groove of the duplex, followed directly by aquation to form the monoaqua monochloro species. There was evidence for two discrete monofunctional adducts, through covalent binding at the guanine N7 sites, and one had distinctly different (1)H/(15)N chemical shifts to those observed previously in analogous reactions. Bifunctional adduct formation followed by binding at a second guanine N7 site with evidence for both the 3'-3' 1,2-GG and 5'-5' 1,6-GG interstrand cross-links in a ratio of 2 : 1. The results show that cross-link preference is kinetically controlled and will depend critically on the reaction conditions, explaining why in a previous reaction of 1 with duplex I the major adduct isolated by HPLC had two simultaneous 3'-3' 1,2-interstrand cross-links.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Long range 1,4 and 1,6-interstrand cross-links formed by a trinuclear platinum complex. Minor groove preassociation affects kinetics and mechanism of cross-link formation as well as adduct structure.J Am Chem Soc. 2004 Feb 25;126(7):2166-80. doi: 10.1021/ja036105u. J Am Chem Soc. 2004. PMID: 14971952
-
Competitive reactions of interstrand and intrastrand DNA-Pt adducts: A dinuclear-platinum complex preferentially forms a 1,4-interstrand cross-link rather than a 1,2 intrastrand cross-link on binding to a GG 14-mer duplex.Chemistry. 2003 Feb 3;9(3):713-25. doi: 10.1002/chem.200390080. Chemistry. 2003. PMID: 12569464
-
Kinetic analysis of the stepwise formation of a long-range DNA interstrand cross-link by a dinuclear platinum antitumor complex: evidence for aquated intermediates and formation of both kinetically and thermodynamically controlled conformers.J Am Chem Soc. 2001 Feb 21;123(7):1316-26. doi: 10.1021/ja0012772. J Am Chem Soc. 2001. PMID: 11456703
-
Chimeric platinum-polyamines and DNA binding. Kinetics of DNA interstrand cross-link formation by dinuclear platinum complexes with polyamine linkers.J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Apr 25;134(16):7135-46. doi: 10.1021/ja301397h. Epub 2012 Apr 10. J Am Chem Soc. 2012. PMID: 22443454
-
Factors affecting DNA-DNA interstrand cross-links in the antiparallel 3'-3' sense: a comparison with the 5'-5' directional isomer.Chemistry. 2009 Sep 21;15(37):9365-74. doi: 10.1002/chem.200900958. Chemistry. 2009. PMID: 19691069 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Metal-based drugs.Sci Prog. 2014;97(Pt 1):1-19. doi: 10.3184/003685014X13898980185076. Sci Prog. 2014. PMID: 24800466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dinuclear platinum(II) complexes as the pattern for phosphate backbone binding: a new perspective for recognition of binding modes to DNA.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2022 Feb;27(1):65-79. doi: 10.1007/s00775-021-01911-6. Epub 2021 Oct 29. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2022. PMID: 34714401
-
New minor groove covering DNA binding mode of dinuclear Pt(II) complexes with various pyridine-linked bridging ligands and dual anticancer-antiangiogenic activities.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2020 May;25(3):395-409. doi: 10.1007/s00775-020-01770-7. Epub 2020 Mar 11. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 32162071
-
Competitive formation of DNA linkage isomers by a trinuclear platinum complex and the influence of pre-association.Dalton Trans. 2015 Feb 28;44(8):3583-3593. doi: 10.1039/c4dt02942a. Dalton Trans. 2015. PMID: 25407024 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Farrell NP. Drugs of the Future. 2012 in press.
-
- Brabec V, Kaspárková J, Vrána O, Nováková O, Cox JW, Qu Y, Farrell N. Biochemistry. 1999;38:6781–6790. - PubMed
-
- Cox JW, Berners-Price SJ, Davies MS, Qu Y, Farrell N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001;123:1316–1326. - PubMed
-
- Hegmans A, Berners-Price SJ, Davies MS, Thomas DS, Humphreys AS, Farrell N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004;126:2166–2180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

