Large ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in an 18-year-old girl and review of literature
- PMID: 23166172
- PMCID: PMC4543837
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2012-007160
Large ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in an 18-year-old girl and review of literature
Abstract
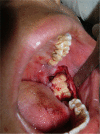
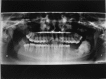
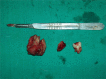
The ameloblastic fibro-odontoma is a rare, benign, mixed neoplasm composed of proliferating odontogenic epithelium, ectomesenchymal tissue and varying degrees of dental hard tissue formation. It occurs exclusively as an intraosseous lesion. It usually exhibits slow growth and is commonly seen in children and young adults. Radiologically, ameloblastic fibro-odontoma appears as a circumscribed radiolucency which may contain radiopaque foci. Most cases of ameloblastic fibro-odontoma exhibit benign behaviour, but cases of malignant transformation have been reported. The treatment modality in most cases involves conservative surgery, but in cases with malignant transformation more radical treatment will be required. A massive ameloblastic fibro-odontoma involving the mandible is being described here with its clinical, radiological and histopathological features.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A massive ameloblastic fibro-odontoma of the maxilla.Indian J Dent Res. 2008 Apr-Jun;19(2):162-4. doi: 10.4103/0970-9290.40474. Indian J Dent Res. 2008. PMID: 18445937
-
Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in children: report of 2 cases.J Dent Child (Chic). 2011 Sep-Dec;78(3):173-7. J Dent Child (Chic). 2011. PMID: 22126932
-
A large ameloblastic fibro-odontoma of the right mandible.Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2007 Jan 1;12(1):E34-7. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2007. PMID: 17195825
-
Ameloblastic Fibro-Odontoma in an Adolescent: A Case Report and Review of Literature.J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2018;42(6):458-460. doi: 10.17796/1053-4625-42.6.10. Epub 2018 Aug 7. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2018. PMID: 30085878 Review.
-
[The ameloblastic fibro-odontoma].Dtsch Zahnarztl Z. 1991 Jan;46(1):71-3. Dtsch Zahnarztl Z. 1991. PMID: 1811980 Review. German.
Cited by
-
A Locally Aggressive Ameloblastic Fibro-Odontoma: A Case Report and Literature Review.Cureus. 2021 Dec 12;13(12):e20366. doi: 10.7759/cureus.20366. eCollection 2021 Dec. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 35036200 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reihcart P, et al. Pathology & genetics of head and neck tumours– World Health organization classification of tumours.v.9.Iarc press 2005.
-
- Sivapathasundharam B, Manikandan R, Sivakumar G, et al. Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma. Indian J Dent Res 2005;16:19–21. - PubMed
-
- Hutt PH. Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma: report of a case. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1982;40:45–8. - PubMed
-
- Howell RM, Burkes EJ. Malignant transformation of ameloblastic fibro-odontoma to ameloblastic fibrosarcoma. Oral Surg 1977;43:391–401. - PubMed
-
- Friedrich RE, Siegert J, Donath Ket al. Recurrent ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in a 10 year old boy. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2001;59:1362–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
