Oligodeoxynucleotide binding to (CTG) · (CAG) microsatellite repeats inhibits replication fork stalling, hairpin formation, and genome instability
- PMID: 23166299
- PMCID: PMC3554215
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01265-12
Oligodeoxynucleotide binding to (CTG) · (CAG) microsatellite repeats inhibits replication fork stalling, hairpin formation, and genome instability
Abstract
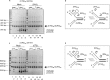
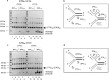
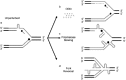
(CTG)(n) · (CAG)(n) trinucleotide repeat (TNR) expansion in the 3' untranslated region of the dystrophia myotonica protein kinase (DMPK) gene causes myotonic dystrophy type 1. However, a direct link between TNR instability, the formation of noncanonical (CTG)(n) · (CAG)(n) structures, and replication stress has not been demonstrated. In a human cell model, we found that (CTG)(45) · (CAG)(45) causes local replication fork stalling, DNA hairpin formation, and TNR instability. Oligodeoxynucleotides (ODNs) complementary to the (CTG)(45) · (CAG)(45) lagging-strand template eliminated DNA hairpin formation on leading- and lagging-strand templates and relieved fork stalling. Prolonged cell culture, emetine inhibition of lagging-strand synthesis, or slowing of DNA synthesis by low-dose aphidicolin induced (CTG)(45) · (CAG)(45) expansions and contractions. ODNs targeting the lagging-strand template blocked the time-dependent or emetine-induced instability but did not eliminate aphidicolin-induced instability. These results show directly that TNR replication stalling, replication stress, hairpin formation, and instability are mechanistically linked in vivo.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Altered replication in human cells promotes DMPK (CTG)(n) · (CAG)(n) repeat instability.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 May;32(9):1618-32. doi: 10.1128/MCB.06727-11. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22354993 Free PMC article.
-
Replication inhibitors modulate instability of an expanded trinucleotide repeat at the myotonic dystrophy type 1 disease locus in human cells.Am J Hum Genet. 2003 Nov;73(5):1092-105. doi: 10.1086/379523. Epub 2003 Oct 21. Am J Hum Genet. 2003. PMID: 14574643 Free PMC article.
-
Replication-dependent instability at (CTG) x (CAG) repeat hairpins in human cells.Nat Chem Biol. 2010 Sep;6(9):652-9. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.416. Epub 2010 Aug 1. Nat Chem Biol. 2010. PMID: 20676085 Free PMC article.
-
Trinucleotide repeat instability: a hairpin curve at the crossroads of replication, recombination, and repair.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2003;100(1-4):7-24. doi: 10.1159/000072836. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2003. PMID: 14526162 Review.
-
Modifiers of CAG/CTG Repeat Instability: Insights from Mammalian Models.J Huntingtons Dis. 2021;10(1):123-148. doi: 10.3233/JHD-200426. J Huntingtons Dis. 2021. PMID: 33579861 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
On the wrong DNA track: Molecular mechanisms of repeat-mediated genome instability.J Biol Chem. 2020 Mar 27;295(13):4134-4170. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV119.007678. Epub 2020 Feb 14. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32060097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Replication fork instability and the consequences of fork collisions from rereplication.Genes Dev. 2016 Oct 15;30(20):2241-2252. doi: 10.1101/gad.288142.116. Genes Dev. 2016. PMID: 27898391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Replication stalling and DNA microsatellite instability.Biophys Chem. 2017 Jun;225:38-48. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2016.11.007. Epub 2016 Nov 22. Biophys Chem. 2017. PMID: 27914716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Replication stress at microsatellites causes DNA double-strand breaks and break-induced replication.J Biol Chem. 2020 Nov 6;295(45):15378-15397. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013495. Epub 2020 Sep 1. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32873711 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothesis: local dNTP depletion as the cause of microsatellite repeat instability during replication (comment on DOI 10.1002/bies.201200128).Bioessays. 2013 Apr;35(4):305. doi: 10.1002/bies.201300026. Bioessays. 2013. PMID: 23494534 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Mirkin SM. 2007. Expandable DNA repeats and human disease. Nature 447: 932–940 - PubMed
-
- Pearson CE, Edamura KN, Cleary JD. 2005. Repeat instability: mechanisms of dynamic mutations. Nat. Rev. Genet. 6: 729–742 - PubMed
-
- Hartenstine MJ, Goodman MF, Petruska J. 2002. Weak strand displacement activity enables human DNA polymerase beta to expand CAG/CTG triplet repeats at strand breaks. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 41379–41389 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
