Therapeutic helminth infection of macaques with idiopathic chronic diarrhea alters the inflammatory signature and mucosal microbiota of the colon
- PMID: 23166490
- PMCID: PMC3499566
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003000
Therapeutic helminth infection of macaques with idiopathic chronic diarrhea alters the inflammatory signature and mucosal microbiota of the colon
Abstract
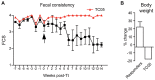
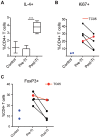
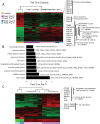
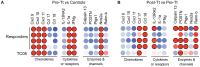
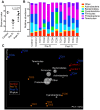
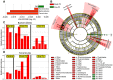
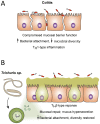
Idiopathic chronic diarrhea (ICD) is a leading cause of morbidity amongst rhesus monkeys kept in captivity. Here, we show that exposure of affected animals to the whipworm Trichuris trichiura led to clinical improvement in fecal consistency, accompanied by weight gain, in four out of the five treated monkeys. By flow cytometry analysis of pinch biopsies collected during colonoscopies before and after treatment, we found an induction of a mucosal T(H)2 response following helminth treatment that was associated with a decrease in activated CD4(+) Ki67+ cells. In parallel, expression profiling with oligonucleotide microarrays and real-time PCR analysis revealed reductions in T(H)1-type inflammatory gene expression and increased expression of genes associated with IgE signaling, mast cell activation, eosinophil recruitment, alternative activation of macrophages, and worm expulsion. By quantifying bacterial 16S rRNA in pinch biopsies using real-time PCR analysis, we found reduced bacterial attachment to the intestinal mucosa post-treatment. Finally, deep sequencing of bacterial 16S rRNA revealed changes to the composition of microbial communities attached to the intestinal mucosa following helminth treatment. Thus, the genus Streptophyta of the phylum Cyanobacteria was vastly increased in abundance in three out of five ICD monkeys relative to healthy controls, but was reduced to control levels post-treatment; by contrast, the phylum Tenericutes was expanded post-treatment. These findings suggest that helminth treatment in primates can ameliorate colitis by restoring mucosal barrier functions and reducing overall bacterial attachment, and also by altering the communities of attached bacteria. These results also define ICD in monkeys as a tractable preclinical model for ulcerative colitis in which these effects can be further investigated.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
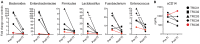
References
-
- Weinstock JV (2006) Helminths and mucosal immune modulation. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1072: 356–364. - PubMed
-
- Summers RW, Elliott DE, Urban JF Jr, Thompson RA, Weinstock JV (2005) Trichuris suis therapy for active ulcerative colitis: a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology 128: 825–832. - PubMed
-
- Smith P, Mangan NE, Walsh CM, Fallon RE, McKenzie AN, et al. (2007) Infection with a helminth parasite prevents experimental colitis via a macrophage-mediated mechanism. J Immunol 178: 4557–4566. - PubMed
-
- Elliott DE, Li J, Blum A, Metwali A, Qadir K, et al. (2003) Exposure to schistosome eggs protects mice from TNBS-induced colitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 284: G385–391. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

