Heterotrimeric G-protein signaling is critical to pathogenic processes in Entamoeba histolytica
- PMID: 23166501
- PMCID: PMC3499586
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003040
Heterotrimeric G-protein signaling is critical to pathogenic processes in Entamoeba histolytica
Abstract
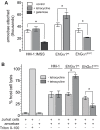
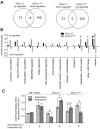
Heterotrimeric G-protein signaling pathways are vital components of physiology, and many are amenable to pharmacologic manipulation. Here, we identify functional heterotrimeric G-protein subunits in Entamoeba histolytica, the causative agent of amoebic colitis. The E. histolytica Gα subunit EhGα1 exhibits conventional nucleotide cycling properties and is seen to interact with EhGβγ dimers and a candidate effector, EhRGS-RhoGEF, in typical, nucleotide-state-selective fashions. In contrast, a crystal structure of EhGα1 highlights unique features and classification outside of conventional mammalian Gα subfamilies. E. histolytica trophozoites overexpressing wildtype EhGα1 in an inducible manner exhibit an enhanced ability to kill host cells that may be wholly or partially due to enhanced host cell attachment. EhGα1-overexpressing trophozoites also display enhanced transmigration across a Matrigel barrier, an effect that may result from altered baseline migration. Inducible expression of a dominant negative EhGα1 variant engenders the converse phenotypes. Transcriptomic studies reveal that modulation of pathogenesis-related trophozoite behaviors by perturbed heterotrimeric G-protein expression includes transcriptional regulation of virulence factors and altered trafficking of cysteine proteases. Collectively, our studies suggest that E. histolytica possesses a divergent heterotrimeric G-protein signaling axis that modulates key aspects of cellular processes related to the pathogenesis of this infectious organism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
G protein signaling in the parasite Entamoeba histolytica.Exp Mol Med. 2013 Mar 22;45(3):e15. doi: 10.1038/emm.2013.30. Exp Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23519208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural determinants of RGS-RhoGEF signaling critical to Entamoeba histolytica pathogenesis.Structure. 2013 Jan 8;21(1):65-75. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2012.11.012. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Structure. 2013. PMID: 23260656 Free PMC article.
-
Self-activating G protein α subunits engage seven-transmembrane regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) proteins and a Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor effector in the amoeba Naegleria fowleri.J Biol Chem. 2022 Aug;298(8):102167. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102167. Epub 2022 Jun 20. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35738399 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the C-Terminal Fragment of Entamoeba histolytica Gal/GalNAc Lectin Intermediate Subunit as a Vaccine Candidate against Amebic Liver Abscess.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016 Jan 29;10(1):e0004419. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004419. eCollection 2016 Jan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016. PMID: 26824828 Free PMC article.
-
The galactose-inhibitable surface lectin of Entamoeba histolytica, a possible candidate for a subunit vaccine to prevent amoebiasis.Behring Inst Mitt. 1997 Mar;(99):112-6. Behring Inst Mitt. 1997. PMID: 9303210 Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence for a bacterial lipopolysaccharide-recognizing G-protein-coupled receptor in the bacterial engulfment by Entamoeba histolytica.Eukaryot Cell. 2013 Nov;12(11):1433-8. doi: 10.1128/EC.00150-13. Epub 2013 Aug 23. Eukaryot Cell. 2013. PMID: 23975887 Free PMC article.
-
Acetylcholine Upregulates Entamoeba histolytica Virulence Factors, Enhancing Parasite Pathogenicity in Experimental Liver Amebiasis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Jan 28;10:586354. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.586354. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33585267 Free PMC article.
-
G protein signaling in the parasite Entamoeba histolytica.Exp Mol Med. 2013 Mar 22;45(3):e15. doi: 10.1038/emm.2013.30. Exp Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23519208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RGS21, a regulator of taste and mucociliary clearance?Laryngoscope. 2014 Mar;124(3):E56-63. doi: 10.1002/lary.24326. Epub 2013 Oct 2. Laryngoscope. 2014. PMID: 23908053 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of virulence of Entamoeba histolytica.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2014;68:493-520. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-091313-103550. Epub 2014 Jun 16. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25002094 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

