C. elegans dopaminergic D2-like receptors delimit recurrent cholinergic-mediated motor programs during a goal-oriented behavior
- PMID: 23166505
- PMCID: PMC3499252
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003015
C. elegans dopaminergic D2-like receptors delimit recurrent cholinergic-mediated motor programs during a goal-oriented behavior
Abstract
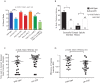
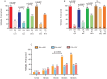
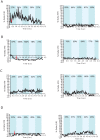
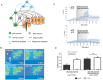
Caenorhabditis elegans male copulation requires coordinated temporal-spatial execution of different motor outputs. During mating, a cloacal circuit consisting of cholinergic sensory-motor neurons and sex muscles maintains the male's position and executes copulatory spicule thrusts at his mate's vulva. However, distinct signaling mechanisms that delimit these behaviors to their proper context are unclear. We found that dopamine (DA) signaling directs copulatory spicule insertion attempts to the hermaphrodite vulva by dampening spurious stimulus-independent sex muscle contractions. From pharmacology and genetic analyses, DA antagonizes stimulatory ACh signaling via the D2-like receptors, DOP-2 and DOP-3, and Gα(o/i) proteins, GOA-1 and GPA-7. Calcium imaging and optogenetics suggest that heightened DA-expressing ray neuron activities coincide with the cholinergic cloacal ganglia function during spicule insertion attempts. D2-like receptor signaling also attenuates the excitability of additional mating circuits to reduce the duration of mating attempts with unproductive and/or inappropriate partners. This suggests that, during wild-type mating, simultaneous DA-ACh signaling modulates the activity threshold of repetitive motor programs, thus confining the behavior to the proper situational context.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DOP-2 D2-Like Receptor Regulates UNC-7 Innexins to Attenuate Recurrent Sensory Motor Neurons during C. elegans Copulation.J Neurosci. 2015 Jul 8;35(27):9990-10004. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0940-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26156999 Free PMC article.
-
A cholinergic-regulated circuit coordinates the maintenance and bi-stable states of a sensory-motor behavior during Caenorhabditis elegans male copulation.PLoS Genet. 2011 Mar;7(3):e1001326. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001326. Epub 2011 Mar 10. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21423722 Free PMC article.
-
G alpha(q)-coupled muscarinic acetylcholine receptors enhance nicotinic acetylcholine receptor signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans mating behavior.J Neurosci. 2007 Feb 7;27(6):1411-21. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4320-06.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17287516 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of sensory motor circuits used in C. elegans male intromission behavior.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Sep;33:42-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.05.006. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24887696 Review.
-
Nematode Tango Milonguero - the C. elegans male's search for the hermaphrodite vulva.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Sep;33:34-41. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.05.009. Epub 2014 May 23. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24862858 Review.
Cited by
-
Latent alterations in swimming behavior by developmental methylmercury exposure are modulated by the homolog of tyrosine hydroxylase in Caenorhabditis elegans.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2021 May-Jun;85:106963. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2021.106963. Epub 2021 Feb 21. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2021. PMID: 33626374 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropeptides and Behaviors: How Small Peptides Regulate Nervous System Function and Behavioral Outputs.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Dec 2;14:786471. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.786471. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34924955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dopamine receptors antagonistically regulate behavioral choice between conflicting alternatives in C. elegans.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 23;9(12):e115985. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115985. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25536037 Free PMC article.
-
Increased dopaminergic neurotransmission results in ethanol dependent sedative behaviors in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Genet. 2021 Feb 1;17(2):e1009346. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009346. eCollection 2021 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 33524034 Free PMC article.
-
Microplastics and Their Impact on Reproduction-Can we Learn From the C. elegans Model?Front Toxicol. 2022 Mar 24;4:748912. doi: 10.3389/ftox.2022.748912. eCollection 2022. Front Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35399297 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beaulieu JM, Sotnikova TD, Marion S, Lefkowitz RJ, Gainetdinov RR, et al. (2005) An Akt/beta-arrestin 2/PP2A signaling complex mediates dopaminergic neurotransmission and behavior. Cell 122: 261–273. - PubMed
-
- Fienberg AA, Hiroi N, Mermelstein PG, Song W, Snyder GL, et al. (1998) DARPP-32: regulator of the efficacy of dopaminergic neurotransmission. Science 281: 838–842. - PubMed
-
- Yan Z, Hsieh-Wilson L, Feng J, Tomizawa K, Allen PB, et al. (1999) Protein phosphatase 1 modulation of neostriatal AMPA channels: regulation by DARPP-32 and spinophilin. Nat Neurosci 2: 13–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

