A Case of Pulmonary MALT Lymphoma Arising from Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonitis
- PMID: 23166544
- PMCID: PMC3492375
- DOI: 10.4046/trd.2012.73.2.115
A Case of Pulmonary MALT Lymphoma Arising from Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonitis
Abstract
Pulmonary mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue-derived (MALT) lymphoma is a rare disease. This disorder is considered to be a model of antigen-driven lymphoma, which is driven either by autoantigens or by chronic inflammatory conditions. Low-grade B-cell MALT lymphoma may develop from a nonneoplastic pulmonary lymphoproliferative disorder, such as lymphocytic interstitial pneumonitis (LIP). A recent estimate predicts that less than 5% of LIP patients acquire malignant, low-grade, B-cell lymphoma. In Korea, there has been no previous report of malignant low-grade, B-cell lymphoma, acquired from LIP. Here, we present the case of a patient with LIP that developed into pulmonary MALT lymphoma, six years after diagnosis.
Keywords: Lung Diseases, Interstitial; Lymphoid Tissue; Lymphoma; Lymphoproliferative Disorders.
Figures



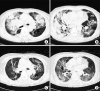
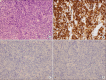
References
-
- Cadranel J, Wislez M, Antoine M. Primary pulmonary lymphoma. Eur Respir J. 2002;20:750–762. - PubMed
-
- Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Stein H, Banks PM, Chan JK, Cleary ML, et al. A revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: a proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Blood. 1994;84:1361–1392. - PubMed
-
- Isaacson P, Wright DH. Extranodal malignant lymphoma arising from mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Cancer. 1984;53:2515–2524. - PubMed
-
- Sminia T, van der Brugge-Gamelkoorn GJ, Jeurissen SH. Structure and function of bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue (BALT) Crit Rev Immunol. 1989;9:119–150. - PubMed
-
- Royer B, Cazals-Hatem D, Sibilia J, Agbalika F, Cayuela JM, Soussi T, et al. Lymphomas in patients with Sjogren's syndrome are marginal zone B-cell neoplasms, arise in diverse extranodal and nodal sites, and are not associated with viruses. Blood. 1997;90:766–775. - PubMed

