Biomarkers of whale shark health: a metabolomic approach
- PMID: 23166652
- PMCID: PMC3499553
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049379
Biomarkers of whale shark health: a metabolomic approach
Abstract
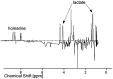
In a search for biomarkers of health in whale sharks and as exploration of metabolomics as a modern tool for understanding animal physiology, the metabolite composition of serum in six whale sharks (Rhincodon typus) from an aquarium collection was explored using (1)H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and direct analysis in real time (DART) mass spectrometry (MS). Principal components analysis (PCA) of spectral data showed that individual animals could be resolved based on the metabolite composition of their serum and that two unhealthy individuals could be discriminated from the remaining healthy animals. The major difference between healthy and unhealthy individuals was the concentration of homarine, here reported for the first time in an elasmobranch, which was present at substantially lower concentrations in unhealthy whale sharks, suggesting that this metabolite may be a useful biomarker of health status in this species. The function(s) of homarine in sharks remain uncertain but it likely plays a significant role as an osmolyte. The presence of trimethylamine oxide (TMAO), another well-known protective osmolyte of elasmobranchs, at 0.1-0.3 mol L(-1) was also confirmed using both NMR and MS. Twenty-three additional potential biomarkers were identified based on significant differences in the frequency of their occurrence between samples from healthy and unhealthy animals, as detected by DART MS. Overall, NMR and MS provided complementary data that showed that metabolomics is a useful approach for biomarker prospecting in poorly studied species like elasmobranchs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
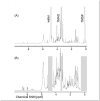
 : unhealthy individual 1
: unhealthy individual 1  : unhealthy individual 2
: unhealthy individual 2  : healthy individual 3 (n = 2)
: healthy individual 3 (n = 2)  : healthy individual 4 (n = 3)
: healthy individual 4 (n = 3)  : healthy individual 5 (n = 5).
: healthy individual 5 (n = 5).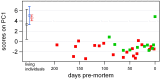
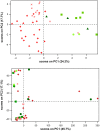
 : unhealthy individual 1
: unhealthy individual 1  : unhealthy individual 2
: unhealthy individual 2  : average for healthy individual 3 (n = 2)
: average for healthy individual 3 (n = 2)  : average for healthy individual 4 (n = 3)
: average for healthy individual 4 (n = 3)  : average for healthy individual 5 (n = 5).
: average for healthy individual 5 (n = 5).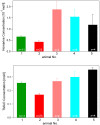
Similar articles
-
Are whale sharks exposed to persistent organic pollutants and plastic pollution in the Gulf of California (Mexico)? First ecotoxicological investigation using skin biopsies.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2017 Sep;199:48-58. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2017.03.002. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28274762
-
Principal component directed partial least squares analysis for combining nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry data in metabolomics: application to the detection of breast cancer.Anal Chim Acta. 2011 Feb 7;686(1-2):57-63. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2010.11.040. Epub 2010 Nov 26. Anal Chim Acta. 2011. PMID: 21237308 Free PMC article.
-
Draft sequencing and assembly of the genome of the world's largest fish, the whale shark: Rhincodon typus Smith 1828.BMC Genomics. 2017 Jul 14;18(1):532. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3926-9. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28709399 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the paradigm: Combining mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance for metabolomics.Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2017 May;100:1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2017.01.001. Epub 2017 Jan 11. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2017. PMID: 28552170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of mass spectrometry-based metabolomics: opportunities and challenges.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1198:3-12. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-1258-2_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25270919 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Simultaneous, untargeted metabolic profiling of polar and nonpolar metabolites by LC-Q-TOF mass spectrometry.Curr Protoc Toxicol. 2013 May;Chapter 4:Unit4.39. doi: 10.1002/0471140856.tx0439s56. Curr Protoc Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23670865 Free PMC article.
-
A metabolic readout of the urine metabolome of COVID-19 patients.Metabolomics. 2023 Jan 24;19(2):7. doi: 10.1007/s11306-023-01971-6. Metabolomics. 2023. PMID: 36694097 Free PMC article.
-
Common fear molecules induce defensive responses in marine prey across trophic levels.Oecologia. 2023 Aug;202(4):655-667. doi: 10.1007/s00442-023-05438-2. Epub 2023 Aug 24. Oecologia. 2023. PMID: 37615742
-
Natural Product Discovery by Direct Analysis in Real Time Mass Spectrometry.Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2019;8(2):S0081. doi: 10.5702/massspectrometry.S0081. Epub 2020 Jan 11. Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2019. PMID: 33299731 Free PMC article.
-
Putative imbalanced amino acid metabolism in rainbow trout long term fed a plant-based diet as revealed by 1H-NMR metabolomics.J Nutr Sci. 2021 Feb 24;10:e13. doi: 10.1017/jns.2021.3. eCollection 2021. J Nutr Sci. 2021. PMID: 33889396 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Colman JG (1997) A review of the biology and ecology of the whale shark. Journal of Fish Biology 51: 1219–1234. - PubMed
-
- Martin RA (2007) A review of behavioural ecology of whale sharks (Rhincodon typus). Fisheries Research 84: 10–16.
-
- Stevens JD (2007) Whale shark (Rhincodon typus) biology and ecology: A review of the primary literature. Fisheries Research 84: 4–9.
-
- Merino M (1997) Upwelling on the Yucatan Shelf: hydrographic evidence. Journal of Marine Systems 13: 101–121.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

