The crystal structure of Arabidopsis VSP1 reveals the plant class C-like phosphatase structure of the DDDD superfamily of phosphohydrolases
- PMID: 23166664
- PMCID: PMC3498132
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049421
The crystal structure of Arabidopsis VSP1 reveals the plant class C-like phosphatase structure of the DDDD superfamily of phosphohydrolases
Abstract
Arabidopsis thaliana vegetative storage proteins, VSP1 and VSP2, are acid phosphatases and belong to the haloacid dehalogenase (HAD) superfamily. In addition to their potential nutrient storage function, they were thought to be involved in plant defense and flower development. To gain insights into the architecture of the protein and obtain clues about its function, we have tested their substrate specificity and solved the structure of VSP1. The acid phosphatase activities of these two enzymes require divalent metal such as magnesium ion. Conversely, the activity of these two enzymes is inhibited by vanadate and molybdate, but is resistant to inorganic phosphate. Both VSP1 and VSP2 did not exhibit remarkable activities to any physiological substrates tested. In the current study, we presented the crystal structure of recombinant VSP1 at 1.8 Å resolution via the selenomethionine single-wavelength anomalous diffraction (SAD). Specifically, an α-helical cap domain on the top of the α/β core domain is found to be involved in dimerization. In addition, despite of the low sequence similarity between VSP1 and other HAD enzymes, the core domain of VSP1 containing conserved active site and catalytic machinery displays a classic haloacid dehalogenase fold. Furthermore, we found that VSP1 is distinguished from bacterial class C acid phosphatase P4 by several structural features. To our knowledge, this is the first study to reveal the crystal structure of plant vegetative storage proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


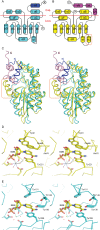
Similar articles
-
The first structure of a bacterial class B Acid phosphatase reveals further structural heterogeneity among phosphatases of the haloacid dehalogenase fold.J Mol Biol. 2004 Jan 16;335(3):761-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2003.10.050. J Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 14687572
-
Structure of recombinant Haemophilus influenzae e (P4) acid phosphatase reveals a new member of the haloacid dehalogenase superfamily.Biochemistry. 2007 Oct 2;46(39):11110-9. doi: 10.1021/bi701016m. Epub 2007 Sep 8. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17824671
-
Structural and functional characterization of a novel phosphatase from the Arabidopsis thaliana gene locus At1g05000.Proteins. 2008 Oct;73(1):241-53. doi: 10.1002/prot.22041. Proteins. 2008. PMID: 18433060 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis thaliana PECP1: enzymatic characterization and structural organization of the first plant phosphoethanolamine/phosphocholine phosphatase.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Feb;1824(2):319-25. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2011.10.003. Epub 2011 Oct 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22024570
-
Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of recombinant VSP1 from Arabidopsis thaliana.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2010 Feb 1;66(Pt 2):201-3. doi: 10.1107/S1744309109053688. Epub 2010 Jan 28. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2010. PMID: 20124723 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Diversification in the inositol tris/tetrakisphosphate kinase (ITPK) family: crystal structure and enzymology of the outlier AtITPK4.Biochem J. 2023 Mar 29;480(6):433-453. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20220579. Biochem J. 2023. PMID: 36896917 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factors Associated with Leaf Senescence in Crops.Plants (Basel). 2019 Oct 14;8(10):411. doi: 10.3390/plants8100411. Plants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31614987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of the pathway structures influencing the temporal response of salicylate and jasmonate defence hormones in Arabidopsis thaliana.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Sep 9;13:952301. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.952301. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36160984 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- DeWald DB, Mason HS, Mullet JE (1992) The soybean vegetative storage proteins VSP alpha and VSP beta are acid phosphatases active on polyphosphates. J Biol Chem 267: 15958–15964. - PubMed
-
- Staswick PE (1994) Storage proteins of vegetative plant-tissue. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 45: 303–322.
-
- Berger S, Bell E, Sadka A, Mullet JE (1995) Arabidopsis thaliana Atvsp is homologous to soybean VspA and VspB, genes encoding vegetative storage protein acid phosphatases, and is regulated similarly by methyl jasmonate, wounding, sugars, light and phosphate. Plant Mol Biol 27: 933–942. - PubMed
-
- Berger S, Mitchell-Olds T, Stotz HU (2002) Local and differential control of vegetative storage protein expression in response to herbivore damage in Arabidopsis thaliana . Physiol Plant 114: 85–91. - PubMed
-
- Guerineau F, Benjdia M, Zhou DX (2003) A jasmonate-responsive element within the A. thaliana vsp1 promoter. J Exp Bot 54: 1153–1162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

