Identification of novel and differentially expressed MicroRNAs of dairy goat mammary gland tissues using solexa sequencing and bioinformatics
- PMID: 23166677
- PMCID: PMC3498112
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049463
Identification of novel and differentially expressed MicroRNAs of dairy goat mammary gland tissues using solexa sequencing and bioinformatics
Abstract
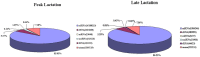
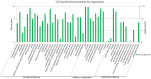
MicroRNAs are small, noncoding RNA molecules that regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level and play an important role in various biological processes. Although most microRNAs expression profiles studies have been performed in humans or rodents, relatively limited knowledge also exists in other mammalian species. The identification of the full repertoire of microRNAs expressed in the lactating mammary gland of Capra hircus would significantly increase our understanding of the physiology of lactating mammary glands. In this study, two libraries were constructed using the lactating mammary gland tissues of Laoshan dairy goats (Capra hircus) during peak and late lactation. Solexa high-throughput sequencing technique and bioinformatics were used to determine the abundance and differential expression of the microRNAs between peak and late lactation. As a result, 19,044,002 and 7,385,833 clean reads were obtained, respectively, and 1,113 conserved known microRNAs and 31 potential novel microRNA candidates were identified. A total of 697 conserved microRNAs were significantly differentially expressed with a P-value<0.01, 272 microRNAs were up-regulated and 425 microRNAs were down-regulated during peak lactation. The results were validated using real-time quantitative RT-PCR. 762,557 annotated mRNA transcripts were predicted as putative target gene candidates. The GO annotation and KEGG pathway analysis suggested that differentially expressed microRNAs were involved in mammary gland physiology, including signal transduction, and cell-cell and cell-extracellular communications. This study provided the first global of the microRNA in Capra hircus and expanded the repertoire of microRNAs. Our results have great significance and value for the elucidation of complex regulatory networks between microRNAs and mRNAs and for the study of mammary gland physiology and lactation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of microRNA in the dairy goat (Capra hircus) mammary gland by Solexa deep-sequencing technology.Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Oct;39(10):9361-71. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-1779-5. Epub 2012 Jul 5. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22763736
-
Comparative transcriptome profiling of dairy goat microRNAs from dry period and peak lactation mammary gland tissues.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52388. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052388. Epub 2012 Dec 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300659 Free PMC article.
-
Genome‑wide integrated analysis demonstrates widespread functions of lncRNAs in mammary gland development and lactation in dairy goats.BMC Genomics. 2020 Mar 23;21(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-6656-3. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32293242 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and analysis of the expression of microRNA from lactating and nonlactating mammary glands of the Chinese swamp buffalo.J Dairy Sci. 2017 Mar;100(3):1971-1986. doi: 10.3168/jds.2016-11461. Epub 2017 Jan 18. J Dairy Sci. 2017. PMID: 28109598 Review.
-
The mammary gland in small ruminants: major morphological and functional events underlying milk production--a review.J Dairy Res. 2014 Aug;81(3):304-18. doi: 10.1017/S0022029914000235. Epub 2014 Jun 5. J Dairy Res. 2014. PMID: 24901899 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of conserved and novel microRNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury of rat using deep sequencing.J Mol Neurosci. 2014 Dec;54(4):671-83. doi: 10.1007/s12031-014-0383-7. Epub 2014 Jul 26. J Mol Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25063377
-
Characterisation and comparison of lactating mouse and bovine mammary gland miRNomes.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 21;9(3):e91938. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091938. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24658750 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of novel and differentially expressed microRNAs between fetal and adult backfat in cattle.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 28;9(2):e90244. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090244. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24587298 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative profiling of differentially expressed microRNAs between the follicular and luteal phases ovaries of goats.Springerplus. 2016 Aug 2;5(1):1233. doi: 10.1186/s40064-016-2902-1. eCollection 2016. Springerplus. 2016. PMID: 27610292 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput sequencing analysis of differentially expressed miRNAs and target genes in ischemia/reperfusion injury and apelin-13 neuroprotection.Neural Regen Res. 2018 Feb;13(2):265-271. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.226397. Neural Regen Res. 2018. PMID: 29557376 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Houbaviy HB, Murray MF, Sharp PA (2003) Embryonic stem cell-specific microRNAs. Dev Cell 5: 351–358. - PubMed
-
- Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Burge CB (2003) Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 115: 787–798. - PubMed
-
- Berezikov E, Guryev V, van de Belt J, Wienholds E, Plasterk RH, et al. (2005) Phylogenetic shadowing and computational identification of human microRNA genes. Cell 120: 21–24. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: 281–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

