MHD free convective boundary layer flow of a nanofluid past a flat vertical plate with Newtonian heating boundary condition
- PMID: 23166688
- PMCID: PMC3499543
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049499
MHD free convective boundary layer flow of a nanofluid past a flat vertical plate with Newtonian heating boundary condition
Abstract
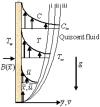
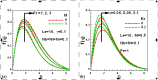
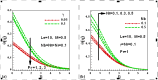
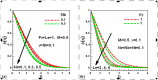
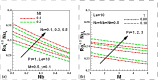
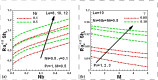
Steady two dimensional MHD laminar free convective boundary layer flows of an electrically conducting Newtonian nanofluid over a solid stationary vertical plate in a quiescent fluid taking into account the Newtonian heating boundary condition is investigated numerically. A magnetic field can be used to control the motion of an electrically conducting fluid in micro/nano scale systems used for transportation of fluid. The transport equations along with the boundary conditions are first converted into dimensionless form and then using linear group of transformations, the similarity governing equations are developed. The transformed equations are solved numerically using the Runge-Kutta-Fehlberg fourth-fifth order method with shooting technique. The effects of different controlling parameters, namely, Lewis number, Prandtl number, buoyancy ratio, thermophoresis, Brownian motion, magnetic field and Newtonian heating on the flow and heat transfer are investigated. The numerical results for the dimensionless axial velocity, temperature and nanoparticle volume fraction as well as the reduced Nusselt and Sherwood number have been presented graphically and discussed. It is found that the rate of heat and mass transfer increase as Newtonian heating parameter increases. The dimensionless velocity and temperature distributions increase with the increase of Newtonian heating parameter. The results of the reduced heat transfer rate is compared for convective heating boundary condition and found an excellent agreement.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of variable thermal conductivity and viscosity on Casson nanofluid flow with convective heating and velocity slip.Heliyon. 2019 Dec 30;6(1):e03076. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e03076. eCollection 2020 Jan. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31909255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nonlinear radiation heat transfer effects in the natural convective boundary layer flow of nanofluid past a vertical plate: a numerical study.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 24;9(9):e103946. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103946. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25251242 Free PMC article.
-
Williamson magneto nanofluid flow over partially slip and convective cylinder with thermal radiation and variable conductivity.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 26;12(1):12727. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16268-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35882915 Free PMC article.
-
Double diffusive magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) mixed convective slip flow along a radiating moving vertical flat plate with convective boundary condition.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 24;9(10):e109404. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109404. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25343360 Free PMC article.
-
MHD forced convective laminar boundary layer flow from a convectively heated moving vertical plate with radiation and transpiration effect.PLoS One. 2013 May 31;8(5):e62664. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062664. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23741295 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer Analysis of a Nanofluid Containing Motile Gyrotactic Micro-Organisms Passing a Nonlinear Stretching Vertical Sheet in the Presence of a Non-Uniform Magnetic Field; Numerical Approach.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 20;11(6):e0157598. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157598. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27322536 Free PMC article.
-
Natural convection flow near a vertical plate that applies a shear stress to a viscous fluid.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 22;8(11):e78352. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078352. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24278110 Free PMC article.
-
Stokes' second problem for magnetohydrodynamics flow in a Burgers' fluid: the cases γ = λ²/4 and γ>λ²/4.PLoS One. 2013 May 8;8(5):e61531. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061531. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23667442 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple slip effects on time dependent axisymmetric flow of magnetized Carreau nanofluid and motile microorganisms.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 22;12(1):14259. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-18344-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35995916 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of variable thermal conductivity and viscosity on Casson nanofluid flow with convective heating and velocity slip.Heliyon. 2019 Dec 30;6(1):e03076. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e03076. eCollection 2020 Jan. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31909255 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abu-Nada E, Hakan F, Oztop, Pop I (2012) Buoyancy induced flow in a nanofluid filled enclosure partially exposed to forced convection. Superlattices and Microstructures 51: 381–395.
-
- Choi SUS (1995) Enhancing Thermal Conductivity of Fluids with Nanoparticles, Developments and Applications of Non-Newtonian Flows. FED-231/MD-vol (66) 99–105.
-
- Choi SUS (2009) Nanofluids: from vision to reality through research. J of Heat Transf 131: 1–9.
-
- Akbarinia A, Abdolzadeh M, Laur R (2011) Critical investigation of heat transfer enhancement using nanofluids in microchannels with slip and non-slip flow regimes. Appl Therm Eng 31: 556–65.
-
- Murshed SMS, et al. (2011) A review of boiling and convective heat transfer with nanofluids. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 15: 2342–2354.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

