Transcriptome analysis of renal ischemia/reperfusion injury and its modulation by ischemic pre-conditioning or hemin treatment
- PMID: 23166714
- PMCID: PMC3498198
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049569
Transcriptome analysis of renal ischemia/reperfusion injury and its modulation by ischemic pre-conditioning or hemin treatment
Abstract
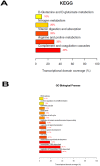
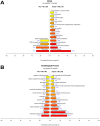
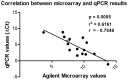
Ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI) is a leading cause of acute renal failure. The definition of the molecular mechanisms involved in renal IRI and counter protection promoted by ischemic pre-conditioning (IPC) or Hemin treatment is an important milestone that needs to be accomplished in this research area. We examined, through an oligonucleotide microarray protocol, the renal differential transcriptome profiles of mice submitted to IRI, IPC and Hemin treatment. After identifying the profiles of differentially expressed genes observed for each comparison, we carried out functional enrichment analysis to reveal transcripts putatively involved in potential relevant biological processes and signaling pathways. The most relevant processes found in these comparisons were stress, apoptosis, cell differentiation, angiogenesis, focal adhesion, ECM-receptor interaction, ion transport, angiogenesis, mitosis and cell cycle, inflammatory response, olfactory transduction and regulation of actin cytoskeleton. In addition, the most important overrepresented pathways were MAPK, ErbB, JAK/STAT, Toll and Nod like receptors, Angiotensin II, Arachidonic acid metabolism, Wnt and coagulation cascade. Also, new insights were gained about the underlying protection mechanisms against renal IRI promoted by IPC and Hemin treatment. Venn diagram analysis allowed us to uncover common and exclusively differentially expressed genes between these two protective maneuvers, underscoring potential common and exclusive biological functions regulated in each case. In summary, IPC exclusively regulated the expression of genes belonging to stress, protein modification and apoptosis, highlighting the role of IPC in controlling exacerbated stress response. Treatment with the Hmox1 inducer Hemin, in turn, exclusively regulated the expression of genes associated with cell differentiation, metabolic pathways, cell cycle, mitosis, development, regulation of actin cytoskeleton and arachidonic acid metabolism, suggesting a pleiotropic effect for Hemin. These findings improve the biological understanding of how the kidney behaves after IRI. They also illustrate some possible underlying molecular mechanisms involved in kidney protection observed with IPC or Hemin treatment maneuvers.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







Similar articles
-
Dual effect of hemin on renal ischemia-reperfusion injury.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Sep 18;503(4):2820-2825. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.046. Epub 2018 Aug 9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 30100067
-
Glutathione S-Transferase and Clusterin, New Players in the Ischemic Preconditioning Renal Protection in a Murine Model of Ischemia and Reperfusion.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2021 Oct 27;55(5):635-650. doi: 10.33594/000000442. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34705356
-
Clearance of damaged mitochondria via mitophagy is important to the protective effect of ischemic preconditioning in kidneys.Autophagy. 2019 Dec;15(12):2142-2162. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1615822. Epub 2019 May 22. Autophagy. 2019. PMID: 31066324 Free PMC article.
-
Remote ischemic preconditioning for kidney protection: GSK3β-centric insights into the mechanism of action.Am J Kidney Dis. 2015 Nov;66(5):846-56. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.06.026. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015. PMID: 26271146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Renal Ischemic Conditioning Strategies.Eur Surg Res. 2015;55(3):151-83. doi: 10.1159/000437352. Epub 2015 Sep 2. Eur Surg Res. 2015. PMID: 26330099 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the Nrf2-Heme Oxygenase-1 Axis after Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(15):2226-2237. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666161027150616. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 27799046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ischemic Preconditioning Alleviates Mouse Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Enhancing Autophagy Activity of Proximal Tubular Cells.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2022 Mar 17;8(3):217-230. doi: 10.1159/000521850. eCollection 2022 May. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35702707 Free PMC article.
-
Intrauterine ischemic reperfusion switches the fetal transcriptional pattern from HIF-1α- to P53-dependent regulation in the murine brain.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 17;9(10):e110577. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110577. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25329663 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Kidney Injury Induced by Mercuric Chloride in Guinea Pigs with In Vivo and In Vitro Experiments.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 18;24(8):7434. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087434. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108594 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of human kidney biopsies unveils emerging acute kidney injury very early after liver graft reperfusion.J Transl Med. 2025 Jun 16;23(1):658. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06695-w. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40524147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liano F, Pascual J (1996) Epidemiology of acute renal failure: a prospective, multicenter, community-based study. Madrid Acute Renal Failure Study Group. Kidney Int 50: 811–818. - PubMed
-
- Brezis M, Epstein FH (1993) Cellular mechanisms of acute ischemic injury in the kidney. Annu Rev Med 44: 27–37. - PubMed
-
- Sutton TA, Molitoris BA (1998) Mechanisms of cellular injury in ischemic acute renal failure. Semin Nephrol 18: 490–497. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

