Inflammatory cascades driven by tumor necrosis factor-alpha play a major role in the progression of acute liver failure and its neurological complications
- PMID: 23166746
- PMCID: PMC3499491
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049670
Inflammatory cascades driven by tumor necrosis factor-alpha play a major role in the progression of acute liver failure and its neurological complications
Abstract
Background/aims: Acute liver failure (ALF) due to ischemic or toxic liver injury is a clinical condition that results from massive loss of hepatocytes and may lead to hepatic encephalopathy (HE), a serious neuropsychiatric complication. Although increased expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) in liver, plasma and brain has been observed, conflicting results exist concerning its roles in drug-induced liver injury and on the progression of HE. The present study aimed to investigate the therapeutic value of etanercept, a TNF-α neutralizing molecule, on the progression of liver injury and HE in mice with ALF resulting from azoxymethane (AOM) hepatotoxicity.
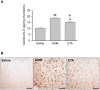
Methods/principal findings: Mice were administered saline or etanercept (10 mg/kg; i.p.) 30 minutes prior to, or up to 6 h after AOM. Etanercept-treated ALF mice were sacrificed in parallel with vehicle-treated comatose ALF mice and controls. AOM induced severe hepatic necrosis, leading to HE, and etanercept administered prior or up to 3 h after AOM significantly delayed the onset of coma stages of HE. Etanercept pretreatment attenuated AOM-induced liver injury, as assessed by histological examination, plasma ammonia and transaminase levels, and by hepatic glutathione content. Peripheral inflammation was significantly reduced by etanercept as shown by decreased plasma IL-6 (4.1-fold; p<0.001) and CD40L levels (3.7-fold; p<0.001) compared to saline-treated ALF mice. Etanercept also decreased IL-6 levels in brain (1.2-fold; p<0.05), attenuated microglial activation (assessed by OX-42 immunoreactivity), and increased brain glutathione concentrations.
Conclusions: These results indicate that systemic sequestration of TNF-α attenuates both peripheral and cerebral inflammation leading to delayed progression of liver disease and HE in mice with ALF due to toxic liver injury. These results suggest that etanercept may provide a novel therapeutic approach for the management of ALF patients awaiting liver transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Ichai P, Samuel D (2008) Etiology and prognosis of fulminant hepatitis in adults. Liver Transpl 14 Suppl 2: S67–79. - PubMed
-
- Acharya SK, Batra Y, Hazari S, Choudhury V, Panda SK, et al. (2002) Etiopathogenesis of acute hepatic failure: Eastern versus Western countries. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 17 Suppl 3: S268–273. - PubMed
-
- Ferenci P, Lockwood A, Mullen K, Tarter R, Weissenborn K, et al. (2002) Hepatic encephalopathy–definition, nomenclature, diagnosis, and quantification: final report of the working party at the 11th World Congresses of Gastroenterology, Vienna, 1998. Hepatology 35: 716–721. - PubMed
-
- Butterworth RF (2011) Neuroinflammation in acute liver failure: Mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets. Neurochem Int 59: 830–836. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

