Whole number, distribution and co-expression of brn3 transcription factors in retinal ganglion cells of adult albino and pigmented rats
- PMID: 23166779
- PMCID: PMC3500320
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049830
Whole number, distribution and co-expression of brn3 transcription factors in retinal ganglion cells of adult albino and pigmented rats
Abstract
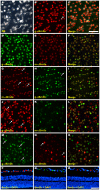
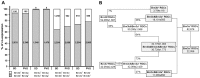
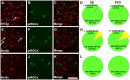
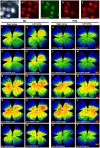
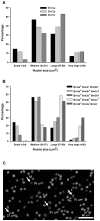
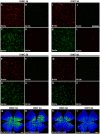
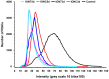
The three members of the Pou4f family of transcription factors: Pou4f1, Pou4f2, Pou4f3 (Brn3a, Brn3b and Brn3c, respectively) play, during development, essential roles in the differentiation and survival of sensory neurons. The purpose of this work is to study the expression of the three Brn3 factors in the albino and pigmented adult rat. Animals were divided into these groups: i) untouched; ii) fluorogold (FG) tracing from both superior colliculli; iii) FG-tracing from one superior colliculus; iv) intraorbital optic nerve transection or crush. All retinas were dissected as flat-mounts and subjected to single, double or triple immunohistofluorescence The total number of FG-traced, Brn3a, Brn3b, Brn3c or Brn3 expressing RGCs was automatically quantified and their spatial distribution assessed using specific routines. Brn3 factors were studied in the general RGC population, and in the intrinsically photosensitive (ip-RGCs) and ipsilateral RGC sub-populations. Our results show that: i) 70% of RGCs co- express two or three Brn3s and the remaining 30% express only Brn3a (26%) or Brn3b; ii) the most abundant Brn3 member is Brn3a followed by Brn3b and finally Brn3c; iii) Brn3 a-, b- or c- expressing RGCs are similarly distributed in the retina; iv) The vast majority of ip-RGCs do not express Brn3; v) The main difference between both rat strains was found in the population of ipsilateral-RGCs, which accounts for 4.2% and 2.5% of the total RGC population in the pigmented and albino strain, respectively. However, more ipsilateral-RGCs express Brn3 factors in the albino than in the pigmented rat; vi) RGCs that express only Brn3b and RGCs that co-express the three Brn3 members have the biggest nuclei; vii) After axonal injury the level of Brn3a expression in the surviving RGCs decreases compared to control retinas. Finally, this work strengthens the validity of Brn3a as a marker to identify and quantify rat RGCs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic interactions between Brn3 transcription factors in retinal ganglion cell type specification.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 8;8(10):e76347. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076347. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24116103 Free PMC article.
-
Morphologies of mouse retinal ganglion cells expressing transcription factors Brn3a, Brn3b, and Brn3c: analysis of wild type and mutant cells using genetically-directed sparse labeling.Vision Res. 2011 Jan 28;51(2):269-79. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2010.08.039. Epub 2010 Sep 6. Vision Res. 2011. PMID: 20826176 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of retinal ganglion cell types and brain nuclei expressing the transcription factor Brn3c/Pou4f3 using a Cre recombinase knock-in allele.J Comp Neurol. 2021 Jun;529(8):1926-1953. doi: 10.1002/cne.25065. Epub 2020 Nov 10. J Comp Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33135183 Free PMC article.
-
Retinal neurodegeneration in experimental glaucoma.Prog Brain Res. 2015;220:1-35. doi: 10.1016/bs.pbr.2015.04.008. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Prog Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 26497783 Review.
-
Methods to Identify Rat and Mouse Retinal Ganglion Cells in Retinal Flat-Mounts.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2708:175-194. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3409-7_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37558971 Review.
Cited by
-
Inner retinal injury in experimental glaucoma is prevented upon AAV mediated Shp2 silencing in a caveolin dependent manner.Theranostics. 2021 Apr 15;11(13):6154-6172. doi: 10.7150/thno.55472. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33995651 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental and functional expression of miRNA-stability related genes in the nervous system.PLoS One. 2013 May 20;8(5):e56908. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056908. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23700402 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the neuroprotective efficacy of the gramine derivative ITH12657 against NMDA-induced excitotoxicity in the rat retina.Front Neuroanat. 2024 Feb 13;18:1335176. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2024.1335176. eCollection 2024. Front Neuroanat. 2024. PMID: 38415017 Free PMC article.
-
Pan-retinal ganglion cell markers in mice, rats, and rhesus macaques.Zool Res. 2023 Jan 18;44(1):226-248. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2022.308. Zool Res. 2023. PMID: 36594396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and axonal transport 1 and 2 weeks after 8 hours of acute intraocular pressure elevation in rats.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Feb 4;55(2):674-87. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-12811. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 24398096 Free PMC article.
References
-
- He X, Treacy MN, Simmons DM, Ingraham HA, Swanson LW, et al. (1989) Expression of a large family of POU-domain regulatory genes in mammalian brain development. Nature 340: 35–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

