Interferon-β induces hepatocyte growth factor in monocytes of multiple sclerosis patients
- PMID: 23166786
- PMCID: PMC3498184
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049882
Interferon-β induces hepatocyte growth factor in monocytes of multiple sclerosis patients
Abstract
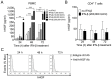
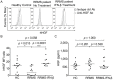
Interferon-β is a first-line therapy used to prevent relapses in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. The clinical benefit of interferon-β in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis is attributed to its immunomodulatory effects on inflammatory mediators and T cell reactivity. Here, we evaluated the production of hepatocyte growth factor, a neuroprotective and neuroinflammation-suppressive mediator, by peripheral blood mononuclear cells collected from interferon-β--treated relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis patients, relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis patients not treated with interferon-β, and healthy volunteers. Using intracellular flow cytometry analysis, increased production of hepatocyte growth factor was observed in circulating CD14(+) monocytes from patients undergoing long-term treatment with interferon-β versus untreated patients. Complementary in vitro studies confirmed that treatment with interferon-β induced rapid and transient transcription of the hepatocyte growth factor gene in CD14(+) monocytes and that intracellular and secreted monocytic hepatocyte growth factor protein levels were markedly stimulated by interferon-β treatment. Additional exploration revealed that "pro-inflammatory" (CD14(+)CD16(+)) monocytes produced similar levels of hepatocyte growth factor in response to interferon-β as "classical" (CD14(+)CD16(-)) monocytes, and that CD14(+) monocytes but not CD4(+) T cells express the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met. Our findings suggest that interferon-β may mediate some of its therapeutic effects in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis through the induction of hepatocyte growth factor by blood monocytes by coupling immune regulation and neuroprotection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Reduced production of noggin by immune cells of patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis.J Neuroimmunol. 2011 Mar;232(1-2):171-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2010.10.007. Epub 2010 Nov 26. J Neuroimmunol. 2011. PMID: 21111488
-
Immunoglobulin-like transcript 3, an inhibitor of T cell activation, is reduced on blood monocytes during multiple sclerosis relapses and is induced by interferon beta-1b.Mult Scler. 2010 Jan;16(1):30-8. doi: 10.1177/1352458509352794. Epub 2009 Dec 9. Mult Scler. 2010. PMID: 20007427
-
Monocyte and Lymphocyte Activation and Regulation in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Therapy Effects.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019 Sep;14(3):413-422. doi: 10.1007/s11481-018-09832-z. Epub 2019 Jan 16. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30649665
-
IFN-beta1b induces transient and variable gene expression in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis patients independent of neutralizing antibodies or changes in IFN receptor RNA expression.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2008 May;28(5):317-31. doi: 10.1089/jir.2007.0131. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2008. PMID: 18547162
-
An inventory of short term and long term changes in gene expression under interferon β treatment of relapsing remitting MS patients.Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(29):4475-84. doi: 10.2174/138161212802502215. Curr Pharm Des. 2012. PMID: 22612748 Review.
Cited by
-
An in vitro coculture system of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells with hepatocellular carcinoma-derived cells for predicting drug-induced liver injury.Arch Toxicol. 2021 Jan;95(1):149-168. doi: 10.1007/s00204-020-02882-4. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Arch Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 32816093
-
Neuroinflammation and Neurodegenerative Diseases: How Much Do We Still Not Know?Brain Sci. 2023 Dec 23;14(1):19. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14010019. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 38248234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The neurotrophic hepatocyte growth factor attenuates CD8+ cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activity.J Neuroinflammation. 2013 Dec 17;10:154. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-10-154. J Neuroinflammation. 2013. PMID: 24344806 Free PMC article.
-
IFN-β Overexpressing Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Mitigate Alcohol-Induced Liver Damage and Gut Permeability.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 4;25(15):8509. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158509. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39126076 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting HGF/c-Met Axis Decreases Circulating Regulatory T Cells Accumulation in Gastric Cancer Patients.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 5;13(21):5562. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215562. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771724 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sospedra M, Martin R (2005) Immunology of multiple sclerosis. Annu Rev Immunol 23: 683–747. - PubMed
-
- Hemmer B, Hartung HP (2007) Toward the development of rational therapies in multiple sclerosis: what is on the horizon? Ann Neurol 62: 314–326. - PubMed
-
- Ebens A, Brose K, Leonardo ED, Hanson MG Jr, Bladt F, et al. (1996) Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor is an axonal chemoattractant and a neurotrophic factor for spinal motor neurons. Neuron 17: 1157–1172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

