Acetaminophen induces human neuroblastoma cell death through NFKB activation
- PMID: 23166834
- PMCID: PMC3500330
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050160
Acetaminophen induces human neuroblastoma cell death through NFKB activation
Abstract
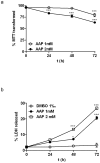
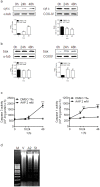
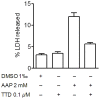
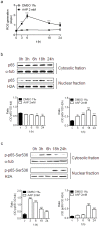
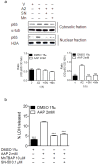
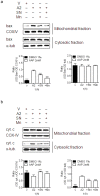
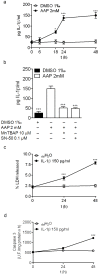
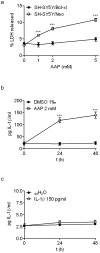
Neuroblastoma resistance to apoptosis may contribute to the aggressive behavior of this tumor. Therefore, it would be relevant to activate endogenous cellular death mechanisms as a way to improve neuroblastoma therapy. We used the neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell line as a model to study the mechanisms involved in acetaminophen (AAP)-mediated toxicity by measuring CYP2E1 enzymatic activity, NFkB p65 subunit activation and translocation to the nucleus, Bax accumulation into the mitochondria, cytochrome c release and caspase activation. AAP activates the intrinsic death pathway in the SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell line. AAP metabolism is partially responsible for this activation, because blockade of the cytochrome CYP2E1 significantly reduced but did not totally prevent, AAP-induced SH-SY5Y cell death. AAP also induced NFkB p65 activation by phosphorylation and its translocation to the nucleus, where NFkB p65 increased IL-1β production. This increase contributed to neuroblastoma cell death through a mechanism involving Bax accumulation into the mitochondria, cytochrome c release and caspase3 activation. Blockade of NFkB translocation to the nucleus by the peptide SN50 prevented AAP-mediated cell death and IL-1β production. Moreover, overexpression of the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-x(L) did not decrease AAP-mediated IL-1β production, but prevented both AAP and IL-1β-mediated cell death. We also confirmed the AAP toxic actions on SK-N-MC neuroepithelioma and U87MG glioblastoma cell lines. The results presented here suggest that AAP activates the intrinsic death pathway in neuroblastoma cells through a mechanism involving NFkB and IL-1β.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acetaminophen induces apoptosis of C6 glioma cells by activating the c-Jun NH(2)-terminal protein kinase-related cell death pathway.Mol Pharmacol. 2001 Oct;60(4):847-56. Mol Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11562448
-
Acetaminophen potentiates staurosporine-induced death in a human neuroblastoma cell line.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Mar;150(5):577-85. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706993. Epub 2007 Jan 22. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17245372 Free PMC article.
-
ROS production is essential for the apoptotic function of E2F1 in pheochromocytoma and neuroblastoma cell lines.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51544. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051544. Epub 2012 Dec 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23251571 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of diallyl disulfide against acetaminophen-induced nephrotoxicity: A possible role of CYP2E1 and NF-κB.Food Chem Toxicol. 2017 Apr;102:156-165. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2017.02.021. Epub 2017 Feb 17. Food Chem Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28219698
-
The chemical biology of IL-12 production via the non-canonical NFkB pathway.RSC Chem Biol. 2020 Jul 22;1(4):166-176. doi: 10.1039/d0cb00022a. eCollection 2020 Oct 1. RSC Chem Biol. 2020. PMID: 34458756 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diacerein counteracts acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice via targeting NLRP3/caspase-1/IL-1β and IL-4/MCP-1 signaling pathways.Arch Pharm Res. 2022 Mar;45(3):142-158. doi: 10.1007/s12272-022-01373-7. Epub 2022 Mar 4. Arch Pharm Res. 2022. PMID: 35244883 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting Neuroblastoma: Nrf2, NF-κB and Phox2B as a Promising Network in Neuroblastoma.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Apr 6;46(4):3193-3208. doi: 10.3390/cimb46040200. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38666930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating the potential of Shikonin as a novel hypertrophic scar treatment.J Biomed Sci. 2015 Aug 16;22(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s12929-015-0172-9. J Biomed Sci. 2015. PMID: 26275605 Free PMC article.
-
The Bioactive Extract of Pinnigorgia sp. Induces Apoptosis of Hepatic Stellate Cells via ROS-ERK/JNK-Caspase-3 Signaling.Mar Drugs. 2018 Jan 9;16(1):19. doi: 10.3390/md16010019. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29315209 Free PMC article.
-
Myristica fragrans Kernels Prevent Paracetamol-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Inducing Anti-Apoptotic Genes and Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 25;20(4):993. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040993. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30823534 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heck JE, Ritz B, Hung RJ, Hashibe M, Boffetta P (2009) The epidemiology of neuroblastoma: a review. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 23: 125–143. - PubMed
-
- Weinstein JL, Katzenstein HM, Cohn SL (2003) Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of neuroblastoma. Oncologist 8: 278–292. - PubMed
-
- Kaatsch P (2010) Epidemiology of childhood cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 36: 277–285. - PubMed
-
- Haase GM, Perez C, Atkinson JB (1999) Current aspects of biology, risk assessment, and treatment of neuroblastoma. Semin Surg Oncol 16: 91–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

