Building a brain in the gut: development of the enteric nervous system
- PMID: 23167617
- PMCID: PMC3721665
- DOI: 10.1111/cge.12054
Building a brain in the gut: development of the enteric nervous system
Abstract
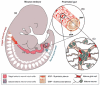
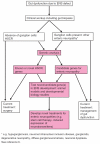
The enteric nervous system (ENS), the intrinsic innervation of the gastrointestinal tract, is an essential component of the gut neuromusculature and controls many aspects of gut function, including coordinated muscular peristalsis. The ENS is entirely derived from neural crest cells (NCC) which undergo a number of key processes, including extensive migration into and along the gut, proliferation, and differentiation into enteric neurons and glia, during embryogenesis and fetal life. These mechanisms are under the molecular control of numerous signaling pathways, transcription factors, neurotrophic factors and extracellular matrix components. Failure in these processes and consequent abnormal ENS development can result in so-called enteric neuropathies, arguably the best characterized of which is the congenital disorder Hirschsprung disease (HSCR), or aganglionic megacolon. This review focuses on the molecular and genetic factors regulating ENS development from NCC, the clinical genetics of HSCR and its associated syndromes, and recent advances aimed at improving our understanding and treatment of enteric neuropathies.
© 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Furness JB. The enteric nervous system. Blackwell Publishing; Oxford: 2006.
-
- Gershon MD. The enteric nervous system: a second brain. Hosp Pract(Off Ed) 1999;34:31–2. 35–8, 41–2. - PubMed
-
- Schemann M. Control of gastrointestinal motility by the “gut brain”-the enteric nervous system. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005;41(Suppl. 1):S4–S6. - PubMed
-
- Brookes SJ. Classes of enteric nerve cells in the guinea-pig small intestine. Anat Rec. 2001;262:58–70. - PubMed
-
- De Giorgio R, Camilleri M. Human enteric neuropathies: morphology and molecular pathology. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2004;16:515–531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

