Midwall ejection fraction for assessing systolic performance of the hypertrophic left ventricle
- PMID: 23167789
- PMCID: PMC3552820
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-7120-10-45
Midwall ejection fraction for assessing systolic performance of the hypertrophic left ventricle
Abstract
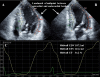
Background: In patients with left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), LV midwall fractional shortening (FS) is used as a measure of LV systolic performance that is more physiologically appropriate than conventional FS. For evaluation of LV volume and ejection fraction (EF), 2-dimensional (2D) echocardiography is more accurate than M-mode echocardiography. The purpose of this study was to assess systolic performance by midwall EF using 2D speckle tracking echocardiography (STE).
Methods: Sixty patients were enrolled in the study. Patients were divided into two groups with LVH (n = 30) and without LVH (control group, n = 30). LV systolic function was compared between the two groups and the relationships of left ventricular mass index (LVMI) with LV systolic parameters, including midwall EF, were investigated.
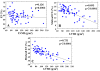
Results: Midwall EF in the LVH group was significantly lower than that in the control group (42.8±4.4% vs. 48.1±4.1%, p <0.0001). Midwall FS was also significantly lower in the LVH group (13.4±2.8% vs. 16.1±1.5%, p <0.0001), but EF did not differ significantly between the two groups. There were significant correlations between midwall EF and LVMI (r=0.731, p <0.0001) and between midwall FS and LVMI (r=0.693, p <0.0001), with midwall EF having the higher correlation.
Conclusions: These results show that midwall EF can be determined using 2D STE. Midwall EF can be used to monitor LV systolic dysfunction, which is not possible with conventional EF. Evaluation of midwall EF may allow assessment of new parameters of LV systolic function in patients with LV geometric variability.
Figures
References
-
- Schussheim AE, Devereux RB, de Simone G, Borer JS, Herrold EM, Laragh JH. Usefulness of subnormal midwall fractional shortening in predicting left ventricular exercise dysfunction in asymptomatic patients with systemic hypertension. Am J Cardiol. 1997;79(8):1070–1074. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9149(97)00049-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Biederman RW, Doyle M, Young AA, Devereux RB, Kortright E, Perry G. et al. Marked regional left ventricular heterogeneity in hypertensive left ventricular hypertrophy patients: a losartan intervention for endpoint reduction in hypertension (LIFE) cardiovascular magnetic resonance and echocardiographic substudy. Hypertension. 2008;52(2):279–286. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.109819. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wachtell K, Rokkedal J, Bella JN, Aalto T, Dahlöf B, Smith G. et al. Effect of electrocardiographic left ventricular hypertrophy on left ventricular systolic function in systemic hypertension (The LIFE Study). Losartan Intervention For Endpoint. Am J Cardiol. 2001;87(1):54–60. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9149(00)01272-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

