How I do it--sole innominate cannulation for acute type A aortic dissection
- PMID: 23167966
- PMCID: PMC3618214
- DOI: 10.1186/1749-8090-7-125
How I do it--sole innominate cannulation for acute type A aortic dissection
Abstract
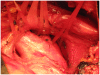
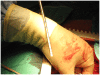
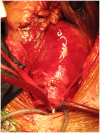
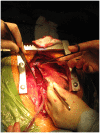
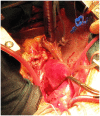
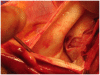
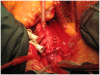
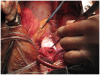
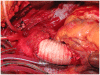
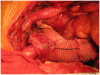
We describe sole direct innominate cannulation for arterial return for establishing both cardiopulmonary bypass and selective antegrade cerebral perfusion in the repair of acute type A dissection and compare it with femoral, axillary, direct aortic and apical cannulations. We believe innominate cannulation has all the advantages of right axillary cannulation and none of its disadvantages. It can be used in all patients in whom innominate artery is not dissected, obstructed, calcified or otherwise diseased.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Is right axillary artery cannulation safe in type A aortic dissection with involvement of the innominate artery?J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016 Sep;152(3):801-807.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2016.04.092. Epub 2016 May 10. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016. PMID: 27239008
-
The use of innominate artery cannulation for antegrade cerebral perfusion in aortic dissection.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2020 Jul 31;15(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s13019-020-01249-1. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2020. PMID: 32736644 Free PMC article.
-
Direct Innominate Artery Cannulation as a Sole Systemic and Cerebral Perfusion Technique in Aortic Surgery.Heart Lung Circ. 2019 Apr;28(4):e67-e70. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2018.08.001. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Heart Lung Circ. 2019. PMID: 30269872
-
Does the arterial cannulation site for circulatory arrest influence stroke risk?Ann Thorac Surg. 2004 Oct;78(4):1274-84; discussion 1274-84. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.04.063. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004. PMID: 15464485 Review.
-
sArterial cannulation to establish cardiopulmonary bypass during surgery for acute aortic dissection.Surg Today. 2020 Nov;50(11):1353-1359. doi: 10.1007/s00595-019-01921-7. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Surg Today. 2020. PMID: 31773278 Review.
Cited by
-
Optimizing aortic arch branch cannulation in acute type A dissection surgery: a minimally invasive approach.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 May 16;12:1549736. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1549736. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40454235 Free PMC article.
-
Innominate truncal and arch blowout with left hemiparesis and right hemothorax followed by delayed cheese-wire perforation of innominate graft.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2013 Apr 23;8:109. doi: 10.1186/1749-8090-8-109. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2013. PMID: 23618057 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Innominate Artery Cannulation Strategy in Acute Type A Aortic Dissection: Better Perfusion, Better Results.J Clin Med. 2023 Apr 13;12(8):2851. doi: 10.3390/jcm12082851. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37109188 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential ruptures of penetrating atherosclerotic ulcers of ascending aorta, aortic arch and descending thoracic aorta.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2020 Oct 6;15(1):298. doi: 10.1186/s13019-020-01311-y. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2020. PMID: 33023614 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baue AE. Glenn’s thoracic and cardiovascular surgery. 6th edn vol 2. Stanford, CT: Appleton and Lange; 1996. Dissections of the aorta; pp. 2273–2274.
-
- Debakey ME, McCollum CH, Crawford ES. Dissection and dissecting aneurysms of aorta: twenty year follow up of five hundred and twenty seven patients treated surgically. Surgery. 1982;92:1118–1134. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

