Distinct roles of Ser-764 and Lys-773 at the N terminus of von Willebrand factor in complex assembly with coagulation factor VIII
- PMID: 23168412
- PMCID: PMC3537036
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.400572
Distinct roles of Ser-764 and Lys-773 at the N terminus of von Willebrand factor in complex assembly with coagulation factor VIII
Abstract
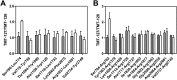
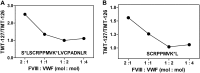
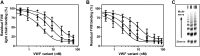
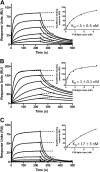
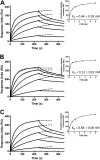
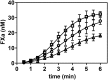
Complex formation between coagulation factor VIII (FVIII) and von Willebrand factor (VWF) is of critical importance to protect FVIII from rapid in vivo clearance and degradation. We have now employed a chemical footprinting approach to identify regions on VWF involved in FVIII binding. To this end, lysine amino acid residues of VWF were chemically modified in the presence of FVIII or activated FVIII, which does not bind VWF. Nano-LC-MS analysis showed that the lysine residues of almost all identified VWF peptides were not differentially modified upon incubation of VWF with FVIII or activated FVIII. However, Lys-773 of peptide Ser-766-Leu-774 was protected from chemical modification in the presence of FVIII. In addition, peptide Ser-764-Arg-782, which comprises the first 19 amino acid residues of mature VWF, showed a differential modification of both Lys-773 and the α-amino group of Ser-764. To verify the role of Lys-773 and the N-terminal Ser-764 in FVIII binding, we employed VWF variants in which either Lys-773 or Ser-764 was replaced with Ala. Surface plasmon resonance analysis and competition studies revealed that VWF(K773A) exhibited reduced binding to FVIII and the FVIII light chain, which harbors the VWF-binding site. In contrast, VWF(S764A) revealed more effective binding to FVIII and the FVIII light chain compared with WT VWF. The results of our study show that the N terminus of VWF is critical for the interaction with FVIII and that Ser-764 and Lys-773 have opposite roles in the binding mechanism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The D' domain of von Willebrand factor requires the presence of the D3 domain for optimal factor VIII binding.Biochem J. 2018 Sep 11;475(17):2819-2830. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20180431. Biochem J. 2018. PMID: 30111575
-
The acidic region of the factor VIII light chain and the C2 domain together form the high affinity binding site for von willebrand factor.J Biol Chem. 1997 Jul 18;272(29):18007-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.29.18007. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9218428
-
A role for the C2 domain of factor VIII in binding to von Willebrand factor.J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11601-5. J Biol Chem. 1994. PMID: 7512568
-
Factor VIII and von Willebrand factor--too sweet for their own good.Haemophilia. 2010 Jul;16 Suppl 5:194-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2516.2010.02320.x. Haemophilia. 2010. PMID: 20590881 Review.
-
Physiological Roles of the von Willebrand Factor-Factor VIII Interaction.Subcell Biochem. 2020;94:437-464. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-41769-7_18. Subcell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32189311 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular determinants of the factor VIII/von Willebrand factor complex revealed by BIVV001 cryo-electron microscopy.Blood. 2021 May 27;137(21):2970-2980. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020009197. Blood. 2021. PMID: 33569592 Free PMC article.
-
A von Willebrand factor fragment containing the D'D3 domains is sufficient to stabilize coagulation factor VIII in mice.Blood. 2014 Jul 17;124(3):445-52. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-11-540534. Epub 2014 May 21. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24850761 Free PMC article.
-
D' domain region Arg782-Cys799 of von Willebrand factor contributes to factor VIII binding.Haematologica. 2020 Jun;105(6):1695-1703. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2019.221994. Epub 2019 Sep 26. Haematologica. 2020. PMID: 31558672 Free PMC article.
-
Von Willebrand factor and hematogenous cancer metastasis under flow.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Aug 30;12:1435718. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1435718. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39282473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On the versatility of von Willebrand factor.Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2013 Jul 10;5(1):e2013046. doi: 10.4084/MJHID.2013.046. Print 2013. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23936617 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schneppenheim R., Budde U. (2011) von Willebrand factor: the complex molecular genetics of a multidomain and multifunctional protein. J. Thromb. Haemost. 9, 209–215 - PubMed
-
- Fay P. J. (2006) Factor VIII structure and function. Int. J. Hematol. 83, 103–108 - PubMed
-
- Morfini M., Mannucci P. M., Tenconi P. M., Longo G., Mazzucconi M. G., Rodeghiero F., Ciavarella N., De Rosa V., Arter A. (1993) Pharmacokinetics of monoclonally-purified and recombinant factor VIII in patients with severe von Willebrand disease. Thromb. Haemost. 70, 270–272 - PubMed
-
- Lenting P. J., Donath M. J., van Mourik J. A., Mertens K. (1994) Identification of a binding site for blood coagulation factor IXa on the light chain of human factor VIII. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 7150–7155 - PubMed
-
- Jacquemin M. (2009) Factor VIII-von Willebrand factor binding defects in autosomal recessive von Willebrand disease type Normandy and in mild hemophilia A. New insights into factor VIII-von Willebrand factor interactions. Acta Haematol. 121, 102–105 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

