Mrp1 is essential for sphingolipid signaling to p-glycoprotein in mouse blood-brain and blood-spinal cord barriers
- PMID: 23168528
- PMCID: PMC3587808
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2012.174
Mrp1 is essential for sphingolipid signaling to p-glycoprotein in mouse blood-brain and blood-spinal cord barriers
Abstract
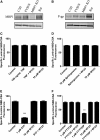
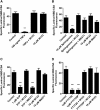
At the blood-brain and blood-spinal cord barriers, P-glycoprotein, an ATP-driven drug efflux pump, is a major obstacle to central nervous system (CNS) pharmacotherapy. Recently, we showed that signaling through tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), sphingolipids, and sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1PR1) rapidly and reversibly reduced basal P-glycoprotein transport activity in the rat blood-brain barrier. The present study extends those findings to the mouse blood-brain and blood-spinal cord barriers and, importantly, identifies multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (Mrp1, Abcc1) as the transporter that mediates S1P efflux from brain and spinal cord endothelial cells. In brain and spinal cord capillaries isolated from wild-type mice, TNF-α, sphingosine, S1P, the S1PR agonist fingolimod (FTY720), and its active, phosphorylated metabolite, FTY720P, reduced P-glycoprotein transport activity; these effects were abolished by a specific S1PR1 antagonist. In brain and spinal cord capillaries isolated from Mrp1-null mice, neither TNF-α nor sphingosine nor FTY720 reduced P-glycoprotein transport activity. However, S1P and FTY720P had the same S1PR1-dependent effects on transport activity as in capillaries from wild-type mice. Thus, deletion of Mrp1 alone terminated endogenous signaling to S1PR1. These results identify Mrp1 as the transporter essential for S1P efflux from the endothelial cells and thus for inside-out S1P signaling to P-glycoprotein at the blood-brain and blood-spinal cord barriers.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Targeting blood-brain barrier sphingolipid signaling reduces basal P-glycoprotein activity and improves drug delivery to the brain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Sep 25;109(39):15930-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1203534109. Epub 2012 Sep 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22949658 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingolipid signaling reduces basal P-glycoprotein activity in renal proximal tubule.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014 Mar;348(3):459-64. doi: 10.1124/jpet.113.210641. Epub 2014 Jan 2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014. PMID: 24385389 Free PMC article.
-
The development and maintenance of paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain require activation of the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor subtype 1.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jul 25;289(30):21082-97. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.569574. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24876379 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P): Physiology and the effects of S1P receptor modulation.Neurology. 2011 Feb 22;76(8 Suppl 3):S3-8. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e31820d5ec1. Neurology. 2011. PMID: 21339489 Review.
-
[Role of S1P acting both inside and outside the cells].Seikagaku. 2012 Feb;84(2):92-101. Seikagaku. 2012. PMID: 22550899 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Novel Insights into the Role of HDL-Associated Sphingosine-1-Phosphate in Cardiometabolic Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 12;20(24):6273. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246273. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31842389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular pharmacodynamics of new oral drugs used in the treatment of multiple sclerosis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014 May 19;8:555-68. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S52428. eCollection 2014. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014. PMID: 24876766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune System and Brain/Intestinal Barrier Functions in Psychiatric Diseases: Is Sphingosine-1-Phosphate at the Helm?Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 10;24(16):12634. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612634. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37628815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1, ABCC1), a "multitasking" ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter.J Biol Chem. 2014 Nov 7;289(45):30880-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R114.609248. Epub 2014 Oct 3. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25281745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P-glycoprotein trafficking as a therapeutic target to optimize CNS drug delivery.Adv Pharmacol. 2014;71:25-44. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2014.06.009. Epub 2014 Aug 23. Adv Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25307213 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Okada T, Ding G, Sonoda H, Kajimoto T, Haga Y, Khosrowbeygi A, et al. Involvement of N-terminal-extended form of sphingosine kinase 2 in serum-dependent regulation of cell proliferation and apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:36318–36325. - PubMed
-
- Meyer ZU, Heringdorf D, Liliom K, Schaefer M, Danneberg K, Jaggar JH, et al. Photolysis of intracellular caged sphingosine-1-phosphate causes Ca2+ mobilization independently of G-protein-coupled receptors. FEBS Lett. 2003;554:443–449. - PubMed
-
- Spiegel S, Milstien S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate: an enigmatic signalling lipid. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:397–407. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

