Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis in India: a review
- PMID: 23168700
- PMCID: PMC3516027
Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis in India: a review
Abstract
Background & objectives: Extensively drug resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB) has become a new threat for the control of TB in many countries including India. Its prevalence is not known in India as there is no nation-wide surveillance. However, there have been some reports from various hospitals in the country.
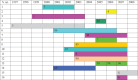
Methods: We have reviewed the studies/information available in the public domain and found data from 10 tertiary care centres in 9 cities in India.
Results: A total of 598 isolates of XDR Mycobacterium tuberculosis have been reported in the studies included. However, the reliability of microbiological methods used in these studies was not checked and thus the XDR-TB data remained invalidated in reference laboratories.
Interpretation & conclusions: Systematic surveillance and containment interventions are urgently needed.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Revised definition of extensively drug resistant tuberculosis. Morb Mortal Weekly Rep. 2006;55:1176.
-
- World Health Organization. Extensively drug resistant tuberculosis (XDR TB): recommendations for prevention and control. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2006;81:430–2. - PubMed
-
- Multidrug and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis: global report on surveillance and response. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2010. World Health Organization.
-
- Thomas A, Ramachandran R, Rehaman F, Jaggarajamma K, Santha T, Selvakumar N, et al. Management of multidrug resistance tuberculosis in the field: Tuberculosis Research Centre experience. Indian J Tuberc. 2007;54:117–24. - PubMed
-
- Ramachandran R, Nalini S, Chandrasekar V, Dave PV, Sanghvi AS, Wares F, et al. Surveillance of drug-resistant tuberculosis in the state of Gujarat, India. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2009;13:1154–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
