Effects of low concentrations of regorafenib and sorafenib on human HCC cell AFP, migration, invasion, and growth in vitro
- PMID: 23169148
- PMCID: PMC3582757
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.24291
Effects of low concentrations of regorafenib and sorafenib on human HCC cell AFP, migration, invasion, and growth in vitro
Abstract
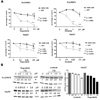
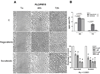
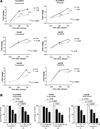
Sorafenib was shown in clinical trial to enhance survival in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients, but with minimal tumor shrinkage. To correlate several indices of HCC growth at various drug concentrations, HCC cells were grown in various low concentrations of two multikinase inhibitors, regorafenib (Stivarga) and sorafenib (Nexavar) and their effects were examined on alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), cell growth, migration, and invasion. In two AFP positive human HCC cell lines, AFP was inhibited at 0.1-1 µM drug concentrations. Cell migration and invasion were also inhibited at similar low drug concentrations. However, 10-fold higher drug concentrations were required to inhibit cell growth in both AFP positive and negative cells. To investigate this concentration discrepancy of effects, cells were then grown for prolonged times and sub-cultured in low drug concentrations and then their growth was re-tested. The growth in these drug-exposed cells was found to be slower than cells without prior drug exposure and they were also more sensitive to subsequent drug challenge. Evidence was also found for changes in cell signaling pathways in these slow-growth cells. Low multikinase inhibitor concentrations thus modulate several aspects of HCC cell biology.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antagonism of sorafenib and regorafenib actions by platelet factors in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines.BMC Cancer. 2014 May 21;14:351. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-351. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24885890 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of VX2 as a Hepatocellular Carcinoma Model: Comparison of the Molecular Reaction of VX2 and HepG2 Tumor Cells to Sorafenib In Vitro.Anticancer Res. 2017 Jan;37(1):87-93. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.11293. Anticancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28011478
-
MiR-21 mediates sorafenib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting autophagy via the PTEN/Akt pathway.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 6;6(30):28867-81. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4814. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26311740 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Regorafenib effects on HCC cell lines by epidermal growth factor.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015 Jun;75(6):1237-1245. doi: 10.1007/s00280-015-2751-6. Epub 2015 Apr 24. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25907508 Free PMC article.
-
Regorafenib for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2017 Jul;17(7):567-576. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2017.1338955. Epub 2017 Jun 9. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2017. PMID: 28580808 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-tumoral activity of single and combined regorafenib treatments in preclinical models of liver and gastrointestinal cancers.Exp Mol Med. 2019 Sep 24;51(9):1-15. doi: 10.1038/s12276-019-0308-1. Exp Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31551425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neratinib augments the lethality of [regorafenib + sildenafil].J Cell Physiol. 2019 Apr;234(4):4874-4887. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27276. Epub 2018 Sep 10. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30203445 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Molecular Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Advances.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 26;14(3):621. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030621. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35158892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Old and New Opportunities.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 20;14(16):4028. doi: 10.3390/cancers14164028. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36011021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy: A Potential Therapeutic Target of Polyphenols in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Feb 29;12(3):562. doi: 10.3390/cancers12030562. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32121322 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adnane L, Trail PA, Taylor I, Wilhelm SM. Sorafenib (BAY 43–9006, Nexavar), a dual-action inhibitor that targets RAF/MEK/ERK pathway in tumor cells and tyrosine kinases VEGFR/PDGFR in tumor vasculature. Methods Enzymol. 2006;407:597–612. - PubMed
-
- Iavarone M, Cabibbo G, Piscaglia F, Zavaglia C, Grieco A, Villa E, Cammà C, Colombo M SOFIA (SoraFenibItalianAssessment) study group. Field-practice study of Sorafenib therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective multicenter study in Italy. Hepatology. 2011;54:2055–2063. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

