Effect on survival of longer intervals between confirmed diagnosis and treatment initiation among low-income women with breast cancer
- PMID: 23169521
- PMCID: PMC3518728
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2012.39.7695
Effect on survival of longer intervals between confirmed diagnosis and treatment initiation among low-income women with breast cancer
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the impact of longer periods between biopsy-confirmed breast cancer diagnosis and the initiation of treatment (Dx2Tx) on survival.
Patients and methods: This study was a noninterventional, retrospective analysis of adult female North Carolina Medicaid enrollees diagnosed with breast cancer from January 1, 2000, through December, 31, 2002, in the linked North Carolina Central Cancer Registry-Medicaid Claims database. Follow-up data were available through July 31, 2006. Cox proportional hazards regression models were constructed to evaluate the impact on survival of delaying treatment ≥ 60 days after a confirmed diagnosis of breast cancer.
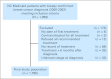
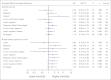
Results: The study cohort consisted of 1,786 low-income, adult women with a mean age of 61.6 years. A large proportion of the patients (44.3%) were racial minorities. Median time from biopsy-confirmed diagnosis to treatment initiation was 22 days. Adjusted Cox proportional hazards regression showed that although Dx2Tx length did not affect survival among those diagnosed at early stage, among late-stage patients, intervals between diagnosis and first treatment ≥ 60 days were associated with significantly worse overall survival (hazard ratio [HR], 1.66; 95% CI, 1.00 to 2.77; P = .05) and breast cancer-specific survival (HR, 1.85; 95% CI, 1.04 to 3.27; P = .04).
Conclusion: One in 10 women waited ≥ 60 days to initiate treatment after a diagnosis of breast cancer. Waiting ≥ 60 days to initiate treatment was associated with a significant 66% and 85% increased risk of overall and breast cancer-related death, respectively, among late-stage patients. Interventions designed to increase the timeliness of receiving breast cancer treatments should target late-stage patients, and clinicians should strive to promptly triage and initiate treatment for patients diagnosed at late stage.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Richards MA, Westcombe AM, Love SB, et al. Influence of delay on survival in patients with breast cancer: A systematic review. Lancet. 1999;353:1119–1126. - PubMed
-
- Afzelius P, Zedeler K, Sommer H, et al. Patient's and doctor's delay in primary breast cancer: Prognostic implications. Acta Oncol. 1994;33:345–351. - PubMed
-
- Sainsbury R, Johnston C, Haward B. Effect on survival of delays in referral of patients with breast-cancer symptoms: A retrospective analysis. Lancet. 1999;353:1132–1135. - PubMed
-
- Delgado DJ, Lin WY, Coffey M. The role of Hispanic race/ethnicity and poverty in breast cancer survival. P R Health Sci J. 1995;14:103–116. - PubMed
-
- Redondo M, Rodrigo I, Pereda T, et al. Prognostic implications of emergency admission and delays in patients with breast cancer. Support Care Cancer. 2009;17:595–599. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

