Heptahelical protein PQLC2 is a lysosomal cationic amino acid exporter underlying the action of cysteamine in cystinosis therapy
- PMID: 23169667
- PMCID: PMC3528584
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1211198109
Heptahelical protein PQLC2 is a lysosomal cationic amino acid exporter underlying the action of cysteamine in cystinosis therapy
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Feb 19;110(8):3197
Abstract
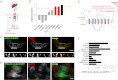
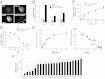
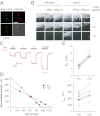
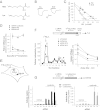
Cystinosin, the lysosomal cystine exporter defective in cystinosis, is the founding member of a family of heptahelical membrane proteins related to bacteriorhodopsin and characterized by a duplicated motif termed the PQ loop. PQ-loop proteins are more frequent in eukaryotes than in prokaryotes; except for cystinosin, their molecular function remains elusive. In this study, we report that three yeast PQ-loop proteins of unknown function, Ypq1, Ypq2, and Ypq3, localize to the vacuolar membrane and are involved in homeostasis of cationic amino acids (CAAs). We also show that PQLC2, a mammalian PQ-loop protein closely related to yeast Ypq proteins, localizes to lysosomes and catalyzes a robust, electrogenic transport that is selective for CAAs and strongly activated at low extracytosolic pH. Heterologous expression of PQLC2 at the yeast vacuole rescues the resistance phenotype of an ypq2 mutant to canavanine, a toxic analog of arginine efficiently transported by PQLC2. Finally, PQLC2 transports a lysine-like mixed disulfide that serves as a chemical intermediate in cysteamine therapy of cystinosis, and PQLC2 gene silencing trapped this intermediate in cystinotic cells. We conclude that PQLC2 and Ypq1-3 proteins are lysosomal/vacuolar exporters of CAAs and suggest that small-molecule transport is a conserved feature of the PQ-loop protein family, in agreement with its distant similarity to SWEET sugar transporters and to the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier. The elucidation of PQLC2 function may help improve cysteamine therapy. It may also clarify the origin of CAA abnormalities in Batten disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Palmieri F. Diseases caused by defects of mitochondrial carriers: A review. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1777(7-8):564–578. - PubMed
-
- Bröer S, Palacín M. The role of amino acid transporters in inherited and acquired diseases. Biochem J. 2011;436(2):193–211. - PubMed
-
- Sagné C, Gasnier B. Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of lysosomal membrane transporters. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2008;31(2):258–266. - PubMed
-
- Fredriksson R, Nordström KJ, Stephansson O, Hägglund MG, Schiöth HB. The solute carrier (SLC) complement of the human genome: Phylogenetic classification reveals four major families. FEBS Lett. 2008;582(27):3811–3816. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

