Sharing of clinical trial data among trialists: a cross sectional survey
- PMID: 23169870
- PMCID: PMC3502744
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.e7570
Sharing of clinical trial data among trialists: a cross sectional survey
Abstract
Objective: To investigate clinical trialists' opinions and experiences of sharing of clinical trial data with investigators who are not directly collaborating with the research team.
Design and setting: Cross sectional, web based survey.
Participants: Clinical trialists who were corresponding authors of clinical trials published in 2010 or 2011 in one of six general medical journals with the highest impact factor in 2011.
Main outcome measures: Support for and prevalence of data sharing through data repositories and in response to individual requests, concerns with data sharing through repositories, and reasons for granting or denying requests.
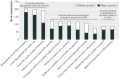
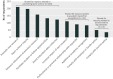
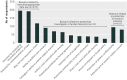
Results: Of 683 potential respondents, 317 completed the survey (response rate 46%). In principle, 236 (74%) thought that sharing de-identified data through data repositories should be required, and 229 (72%) thought that investigators should be required to share de-identified data in response to individual requests. In practice, only 56 (18%) indicated that they were required by the trial funder to deposit the trial data in a repository; of these 32 (57%) had done so. In all, 149 respondents (47%) had received an individual request to share their clinical trial data; of these, 115 (77%) had granted and 56 (38%) had denied at least one request. Respondents' most common concerns about data sharing were related to appropriate data use, investigator or funder interests, and protection of research subjects.
Conclusions: We found strong support for sharing clinical trial data among corresponding authors of recently published trials in high impact general medical journals who responded to our survey, including a willingness to share data, although several practical concerns were identified.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at
Figures
Comment in
-
What about trialists sharing other study materials?BMJ. 2012 Dec 10;345:e8352. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e8352. BMJ. 2012. PMID: 23229066 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Predictors of clinical trial data sharing: exploratory analysis of a cross-sectional survey.Trials. 2014 Oct 2;15:384. doi: 10.1186/1745-6215-15-384. Trials. 2014. PMID: 25277128 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Data Sharing After Implementation of the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors Data Sharing Statement Requirement.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Jan 4;4(1):e2033972. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.33972. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 33507256 Free PMC article.
-
Data-Sharing Statements Requested from Clinical Trials by Public, Environmental, and Occupational Health Journals: Cross-Sectional Study.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Feb 7;27:e64069. doi: 10.2196/64069. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 39919275 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of available studies and dissemination of research using major clinical data sharing platforms.Clin Trials. 2021 Dec;18(6):657-666. doi: 10.1177/17407745211038524. Epub 2021 Aug 18. Clin Trials. 2021. PMID: 34407656 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
How often do cancer researchers make their data and code available and what factors are associated with sharing?BMC Med. 2022 Nov 9;20(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12916-022-02644-2. BMC Med. 2022. PMID: 36352426 Free PMC article.
-
Attitudes towards animal study registries and their characteristics: An online survey of three cohorts of animal researchers.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 6;15(1):e0226443. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226443. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31905203 Free PMC article.
-
Overview and experience of the YODA Project with clinical trial data sharing after 5 years.Sci Data. 2018 Nov 27;5:180268. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2018.268. Sci Data. 2018. PMID: 30480665 Free PMC article.
-
Public Attitudes to Digital Health Research Repositories: Cross-sectional International Survey.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Oct 29;23(10):e31294. doi: 10.2196/31294. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 34714253 Free PMC article.
-
To share or not to share? Expected pros and cons of data sharing in radiological research.Eur Radiol. 2018 Jun;28(6):2328-2335. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5165-5. Epub 2018 Jan 18. Eur Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29349697
References
-
- National Institutes of Health (NIH). Final NIH statement on sharing research data. 2003. http://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/notice-files/NOT-OD-03-032.html (accessed 6 Oct 2012).
-
- Medical Research Council (MRC). MRC policy on research data-sharing. www.mrc.ac.uk/Ourresearch/Ethicsresearchguidance/datasharing/Policy/inde... (accessed 6 Oct 2012).
-
- Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. Our commitment to sharing information. www.gatesfoundation.org/global-health/Pages/our-commitment.aspx (accessed 6 Oct 2012).
-
- Laine C, Goodman SN, Griswold ME, Sox HC. Reproducible research: moving toward research the public can really trust. Ann Intern Med 2007;146:450-3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
