Interleukin 6-preconditioned neural stem cells reduce ischaemic injury in stroke mice
- PMID: 23169920
- PMCID: PMC3501976
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/aws259
Interleukin 6-preconditioned neural stem cells reduce ischaemic injury in stroke mice
Abstract
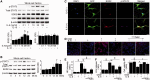
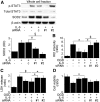
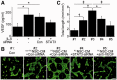
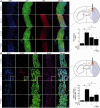
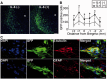
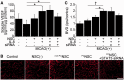
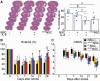
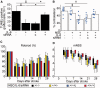
Transplantation of neural stem cells provides a promising therapy for stroke. Its efficacy, however, might be limited because of massive grafted-cell death after transplantation, and its insufficient capability for tissue repair. Interleukin 6 is a pro-inflammatory cytokine involved in the pathogenesis of various neurological disorders. Paradoxically, interleukin 6 promotes a pro-survival signalling pathway through activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. In this study, we investigated whether cellular reprogramming of neural stem cells with interleukin 6 facilitates the effectiveness of cell transplantation therapy in ischaemic stroke. Neural stem cells harvested from the subventricular zone of foetal mice were preconditioned with interleukin 6 in vitro and transplanted into mouse brains 6 h or 7 days after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Interleukin 6 preconditioning protected the grafted neural stem cells from ischaemic reperfusion injury through signal transducer and activator of transcription 3-mediated upregulation of manganese superoxide dismutase, a primary mitochondrial antioxidant enzyme. In addition, interleukin 6 preconditioning induced secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor from the neural stem cells through activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, resulting in promotion of angiogenesis in the ischaemic brain. Furthermore, transplantation of interleukin 6-preconditioned neural stem cells significantly attenuated infarct size and improved neurological performance compared with non-preconditioned neural stem cells. This interleukin 6-induced amelioration of ischaemic insults was abolished by transfecting the neural stem cells with signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 small interfering RNA before transplantation. These results indicate that preconditioning with interleukin 6, which reprograms neural stem cells to tolerate oxidative stress after ischaemic reperfusion injury and to induce angiogenesis through activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, is a simple and beneficial approach for enhancing the effectiveness of cell transplantation therapy in ischaemic stroke.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Minocycline-preconditioned neural stem cells enhance neuroprotection after ischemic stroke in rats.J Neurosci. 2012 Mar 7;32(10):3462-73. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5686-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22399769 Free PMC article.
-
Neural stem cells genetically modified to overexpress cu/zn-superoxide dismutase enhance amelioration of ischemic stroke in mice.Stroke. 2012 Sep;43(9):2423-9. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.656900. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Stroke. 2012. PMID: 22713489 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotection by interleukin-6 is mediated by signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and antioxidative signaling in ischemic stroke.Stroke. 2011 Dec;42(12):3574-9. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.626648. Epub 2011 Sep 22. Stroke. 2011. PMID: 21940958 Free PMC article.
-
Reperfusion and neurovascular dysfunction in stroke: from basic mechanisms to potential strategies for neuroprotection.Mol Neurobiol. 2010 Jun;41(2-3):172-9. doi: 10.1007/s12035-010-8102-z. Epub 2010 Feb 17. Mol Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 20157789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunopharmacological intervention for successful neural stem cell therapy: New perspectives in CNS neurogenesis and repair.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Jan;141(1):21-31. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.08.001. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 23954656 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of IL-6 trans-signaling promotes post-stroke functional recovery in a sex and dose-dependent manner.J Neuroinflammation. 2025 Feb 26;22(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12974-025-03365-y. J Neuroinflammation. 2025. PMID: 40011978 Free PMC article.
-
The stem cell secretome and its role in brain repair.Biochimie. 2013 Dec;95(12):2271-85. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.06.020. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Biochimie. 2013. PMID: 23827856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review Cerebral Ischemic Tolerance and Preconditioning: Methods, Mechanisms, Clinical Applications, and Challenges.Front Neurol. 2020 Sep 18;11:812. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00812. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33071923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preconditioning provides neuroprotection in models of CNS disease: paradigms and clinical significance.Prog Neurobiol. 2014 Mar;114:58-83. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.11.005. Epub 2014 Jan 2. Prog Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24389580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protection of intestinal injury during heat stroke in mice by interleukin-6 pretreatment.J Physiol. 2015 Feb 1;593(3):739-52; discussion 753. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.283416. Epub 2015 Jan 2. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25433073 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bacigaluppi M, Pluchino S, Jametti LP, Kilic E, Kilic Ü, Salani G, et al. Delayed post-ischaemic neuroprotection following systemic neural stem cell transplantation involves multiple mechanisms. Brain. 2009;132:2239–51. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee S, Williamson D, Habib N, Gordon M, Chataway J. Human stem cell therapy in ischaemic stroke: a review. Age Ageing. 2011;40:7–13. - PubMed
-
- Beamer NB, Coull BM, Clark WM, Hazel JS, Silberger JR. Interleukin-6 and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in acute stroke. Ann Neurol. 1995;37:800–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

