Truly resistant hypertension?
- PMID: 23169928
- PMCID: PMC4544918
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2012-007396
Truly resistant hypertension?
Abstract
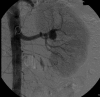
A young man presented with severe hypertension with evidence of both neurological and cardiovascular end-organ damage. Investigation revealed a small right kidney and a left renal artery aneurysm. Significant hypertension persisted even after right nephrectomy. Despite extensive investigation, no evidence was found to implicate the aneurysm in the causation of his high blood pressure. No alternative cause for hypertension was found, yet blood pressure was high even during hospital admission and observed medication dosing with eight antihypertensive agents. Sustained hypertension resulted in worsening left ventricular hypertrophy and he died suddenly at a tragically young age several years after presentation. This gentleman had truly resistant hypertension, a clinical problem which can be very difficult to manage.
Figures
References
-
- Burnier M. Medication adherence and persistence as the cornerstone of effective antihypertensive therapy. Am J Hypertens 2006;19:1190–6. - PubMed
-
- Pfeiffer T, Reiher L, Grabitz K, et al. Reconstruction for renal artery aneurysm: operative techniques and long-term results. J Vasc Surg 2003;37:293–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical