Antioxidant and anti-protease activities of diazepinomicin from the sponge-associated Micromonospora strain RV115
- PMID: 23170078
- PMCID: PMC3497017
- DOI: 10.3390/md10102208
Antioxidant and anti-protease activities of diazepinomicin from the sponge-associated Micromonospora strain RV115
Abstract
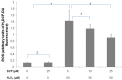
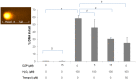
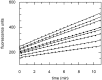
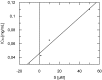
Diazepinomicin is a dibenzodiazepine alkaloid with an unusual structure among the known microbial metabolites discovered so far. Diazepinomicin was isolated from the marine sponge-associated strain Micromonospora sp. RV115 and was identified by spectroscopic analysis and by comparison to literature data. In addition to its interesting preclinical broad-spectrum antitumor potential, we report here new antioxidant and anti-protease activities for this compound. Using the ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assay, a strong antioxidant potential of diazepinomicin was demonstrated. Moreover, diazepinomicin showed a significant antioxidant and protective capacity from genomic damage induced by the reactive oxygen species hydrogen peroxide in human kidney (HK-2) and human promyelocytic (HL-60) cell lines. Additionally, diazepinomicin inhibited the proteases rhodesain and cathepsin L at an IC₅₀ of 70-90 µM. It also showed antiparasitic activity against trypomastigote forms of Trypanosoma brucei with an IC₅₀ of 13.5 µM. These results showed unprecedented antioxidant and anti-protease activities of diazepinomicin, thus further highlighting its potential as a future drug candidate.
Keywords: Micromonospora; actinomycetes; anti-protease; antioxidant; diazepinomicin.
Figures


References
-
- McAlpine J.B., Banskota A.H., Charan R.D., Schlingmann G., Zazopoulos E., Piraee M., Janso J., Bernan V.S., Aouidate M., Farnet C.M., et al. Biosynthesis of diazepinomicin/ECO-4601, a Micromonospora secondary metabolite with a novel ring system. J. Nat. Prod. 2008;71:1585–1590. doi: 10.1021/np800376n. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Campas C. Diazepinomicin. Drug Fut. 2009;34:349–351. doi: 10.1358/dof.2009.034.05.1370797. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

