Rifaximin Plus Levofloxacin-Based Rescue Regimen for the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori
- PMID: 23170149
- PMCID: PMC3493725
- DOI: 10.5009/gnl.2012.6.4.452
Rifaximin Plus Levofloxacin-Based Rescue Regimen for the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori
Abstract
Background/aims: This study assessed the efficacy of a rifaximin plus levofloxacin-based rescue regimen in patients that had failed both triple and quadruple standard regimens for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori.
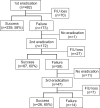
Methods: We treated patients for H. pylori between August 2009 and April 2011. The triple regimen consisted of combined treatment with amoxicillin, clarithromycin, and pantoprazole for 1 week. For failed cases, a quadruple regimen of tetracycline, metronidazole, bismuth dicitrate, and lansoprazole for 1 week was administered. The rescue regimen for persistently refractory cases was rifaximin 200 mg t.i.d., levofloxacin 500 mg q.d., and lansoprazole 15 mg b.i.d. for 1 week.
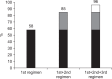
Results: In total, 482 patients were enrolled in this study. The eradication rates associated with the first and second regimens were 58% and 60%, respectively. Forty-seven out of 58 patients who failed with the second-line regimen received rifaximin plus levofloxacin-based third-line therapy. The eradication rate for the third regimen was 65%. The cumulative eradication rates were 58%, 85%, and 96% for each regimen, respectively.
Conclusions: A rifaximin plus levofloxacin-based regimen could be an alternative rescue therapy in patients with resistance to both triple and quadruple regimens for the eradication of H. pylori.
Keywords: Eradication; Helicobacter pylori; Rifaximin.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Second-line rescue treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: Where are we now?World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Oct 28;24(40):4548-4553. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i40.4548. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30386104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Helicobacter pylori Eradication Rates of 2-Week Levofloxacin-Containing Triple Therapy, Levofloxacin-Containing Bismuth Quadruple Therapy, and Standard Bismuth Quadruple Therapy as a First-Line Regimen.Med Princ Pract. 2017;26(6):523-529. doi: 10.1159/000484930. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Med Princ Pract. 2017. PMID: 29131124 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Helicobacter pylori second-line rescue therapy with levofloxacin- and bismuth-containing quadruple therapy, after failure of standard triple or non-bismuth quadruple treatments.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Apr;41(8):768-75. doi: 10.1111/apt.13128. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25703120 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment options for Helicobacter pylori infection when proton pump inhibitor-based triple therapy fails in clinical practice.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1999 Apr;13(4):489-96. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.1999.00504.x. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1999. PMID: 10215733 Clinical Trial.
-
Update on the second-line treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: a narrative review.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2023 Sep 4;16:17562848231192750. doi: 10.1177/17562848231192750. eCollection 2023. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37675247 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rescue Therapy with a Proton Pump Inhibitor Plus Amoxicillin and Rifabutin for Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2015;2015:415648. doi: 10.1155/2015/415648. Epub 2015 May 25. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2015. PMID: 26106411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection in Korea: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Korean Med Sci. 2015 Aug;30(8):1001-9. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2015.30.8.1001. Epub 2015 Jul 15. J Korean Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26240475 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Levofloxacin-Based Third-Line Therapy for the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori in Peptic Ulcer Disease.Gut Liver. 2017 Mar 15;11(2):226-231. doi: 10.5009/gnl16099. Gut Liver. 2017. PMID: 27609487 Free PMC article.
-
Current Status of the Third-Line Helicobacter pylori Eradication.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2018 May 2;2018:6523653. doi: 10.1155/2018/6523653. eCollection 2018. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2018. PMID: 29853863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic efficacy of amoxicillin and rifaximin in patients with small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and Helicobacter pylori infection.Prz Gastroenterol. 2018;13(3):213-217. doi: 10.5114/pg.2018.74228. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Prz Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30302165 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Malfertheiner P, Mégraud F, O'Morain C, et al. Current concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection: the Maastricht 2-2000 Consensus Report. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2002;16:167–180. - PubMed
-
- Scarpignato C. Towards the ideal regimen for Helicobacter pylori eradication: the search continues. Dig Liver Dis. 2004;36:243–247. - PubMed
-
- McLoughlin RM, O'Morain CA, O'Connor HJ. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori: recent advances in treatment. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2005;19:421–427. - PubMed
-
- Candelli M, Nista EC, Carloni E, et al. Treatment of H. pylori infection: a review. Curr Med Chem. 2005;12:375–384. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous