Rifaximin Plus Levofloxacin-Based Rescue Regimen for the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori
- PMID: 23170149
- PMCID: PMC3493725
- DOI: 10.5009/gnl.2012.6.4.452
Rifaximin Plus Levofloxacin-Based Rescue Regimen for the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori
Abstract
Background/aims: This study assessed the efficacy of a rifaximin plus levofloxacin-based rescue regimen in patients that had failed both triple and quadruple standard regimens for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori.
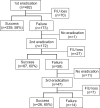
Methods: We treated patients for H. pylori between August 2009 and April 2011. The triple regimen consisted of combined treatment with amoxicillin, clarithromycin, and pantoprazole for 1 week. For failed cases, a quadruple regimen of tetracycline, metronidazole, bismuth dicitrate, and lansoprazole for 1 week was administered. The rescue regimen for persistently refractory cases was rifaximin 200 mg t.i.d., levofloxacin 500 mg q.d., and lansoprazole 15 mg b.i.d. for 1 week.
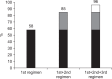
Results: In total, 482 patients were enrolled in this study. The eradication rates associated with the first and second regimens were 58% and 60%, respectively. Forty-seven out of 58 patients who failed with the second-line regimen received rifaximin plus levofloxacin-based third-line therapy. The eradication rate for the third regimen was 65%. The cumulative eradication rates were 58%, 85%, and 96% for each regimen, respectively.
Conclusions: A rifaximin plus levofloxacin-based regimen could be an alternative rescue therapy in patients with resistance to both triple and quadruple regimens for the eradication of H. pylori.
Keywords: Eradication; Helicobacter pylori; Rifaximin.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Malfertheiner P, Mégraud F, O'Morain C, et al. Current concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection: the Maastricht 2-2000 Consensus Report. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2002;16:167–180. - PubMed
-
- Scarpignato C. Towards the ideal regimen for Helicobacter pylori eradication: the search continues. Dig Liver Dis. 2004;36:243–247. - PubMed
-
- McLoughlin RM, O'Morain CA, O'Connor HJ. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori: recent advances in treatment. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2005;19:421–427. - PubMed
-
- Candelli M, Nista EC, Carloni E, et al. Treatment of H. pylori infection: a review. Curr Med Chem. 2005;12:375–384. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous