Primary sterile necrotic cells fail to cross-prime CD8(+) T cells
- PMID: 23170250
- PMCID: PMC3494616
- DOI: 10.4161/onci.21098
Primary sterile necrotic cells fail to cross-prime CD8(+) T cells
Abstract
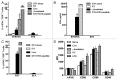
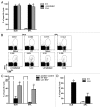
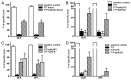
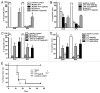
Necrotic cells are known to activate the innate immune system and trigger inflammation by releasing damage associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). However, how necrotic cells influence the induction of antigen-specific CD8(+) T cell-mediated adaptive immune responses under sterile conditions, in the absence of pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), remains poorly understood. Here, we examined antigen-specific CD8(+) T-cell responses to primary sterile necrotic tumor cells both in vitro and in vivo. We found that primary necrotic cells alone fail to generate CD8(+) T cell-dependent immune responses toward cell-associated antigens. We show that necrotic cells trigger CD8(+) T-cell immunity only in the presence of PAMPs or analogs, such as p(dI-dC) and/or unmethylated CpG DNA. The electroporation of tumor cells with these PAMPs prior to necrosis induction triggered antigen-specific CD8(+) T-cell responses through a TLR9/MyD88-dependent pathway. In addition, we found that necrotic cells contain factors that can block the cross-priming of CD8(+) T cells even under non-sterile conditions and can serve as a possible mechanism of immunosuppression. These results suggest that antigen-specific CD8(+) T-cell responses to primary necrotic tumor cells can be induced in the presence of PAMPs and thus have a substantial impact on the development of antitumor vaccination strategies.
Figures

References
-
- Sauter B, Albert ML, Francisco L, Larsson M, Somersan S, Bhardwaj N. Consequences of cell death: exposure to necrotic tumor cells, but not primary tissue cells or apoptotic cells, induces the maturation of immunostimulatory dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 2000;191:423–34. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.3.423. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
