A systematic review of the etiopathogenesis of Kienböck's disease and a critical appraisal of its recognition as an occupational disease related to hand-arm vibration
- PMID: 23171057
- PMCID: PMC3559259
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-13-225
A systematic review of the etiopathogenesis of Kienböck's disease and a critical appraisal of its recognition as an occupational disease related to hand-arm vibration
Erratum in
-
Correction: A systematic review of the etiopathogenesis of Kienböck's disease and a critical appraisal of its recognition as an occupational disease related to hand-arm vibration.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Mar 13;25(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-06850-8. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 38481161 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: We systematically reviewed etiological factors of Kienböck's disease (osteonecrosis of the lunate) discussed in the literature in order to examine the justification for including Kienböck's disease (KD) in the European Listing of Occupational Diseases.
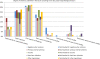
Methods: We searched the Ovid/Medline and the Cochrane Library for articles discussing the etiology of osteonecrosis of the lunate published since the first description of KD in 1910 and up until July 2012 in English, French or German. Literature was classified by the level of evidence presented, the etiopathological hypothesis discussed, and the author's conclusion about the role of the etiopathological hypothesis. The causal relationship between KD and hand-arm vibration was elucidated by the Bradford Hill criteria.
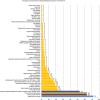
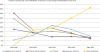
Results: A total of 220 references was found. Of the included 152 articles, 140 (92%) reached the evidence level IV (case series). The four most frequently discussed factors were negative ulnar variance (n=72; 47%), primary arterial ischemia of the lunate (n=63; 41%), trauma (n=63; 41%) and hand-arm vibration (n=53; 35%). The quality of the cohort studies on hand-arm vibration did not permit a meta-analysis to evaluate the strength of an association to KD. Evidence for the lack of consistency, plausibility and coherence of the 4 most frequently discussed etiopathologies was found. No evidence was found to support any of the nine Bradford Hill criteria for a causal relationship between KD and hand-arm vibration.
Conclusions: A systematic review of 220 articles on the etiopathology of KD and the application of the Bradford Hill criteria does not provide sufficient scientific evidence to confirm or refute a causal relationship between KD and hand-arm vibration. This currently suggests that, KD does not comply with the criteria of the International Labour Organization determining occupational diseases. However, research with a higher level of evidence is required to further determine if hand-arm vibration is a risk factor for KD.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interventions to prevent occupational noise-induced hearing loss.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 7;7(7):CD006396. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006396.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28685503 Free PMC article.
-
Causal assessment of occupational bending or twisting and low back pain: results of a systematic review.Spine J. 2010 Jan;10(1):76-88. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2009.06.005. Epub 2009 Jul 23. Spine J. 2010. PMID: 19631589
-
Causal assessment of occupational carrying and low back pain: results of a systematic review.Spine J. 2010 Jul;10(7):628-38. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2010.03.027. Epub 2010 May 5. Spine J. 2010. PMID: 20447872
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Causal assessment of occupational sitting and low back pain: results of a systematic review.Spine J. 2010 Mar;10(3):252-61. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2009.12.005. Epub 2010 Jan 25. Spine J. 2010. PMID: 20097618
Cited by
-
The Etiology and Pathogenesis of Kienböck Disease.J Wrist Surg. 2016 Nov;5(4):248-254. doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1583755. Epub 2016 May 2. J Wrist Surg. 2016. PMID: 27777813 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Case Report on Kienbock's Disease: Diagnostic Hurdles and Surgical Outcomes With Proximal Row Carpectomy.Cureus. 2024 Aug 14;16(8):e66829. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66829. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39280429 Free PMC article.
-
Physio-metabolic and clinical consequences of wearing face masks-Systematic review with meta-analysis and comprehensive evaluation.Front Public Health. 2023 Apr 5;11:1125150. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1125150. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. Retraction in: Front Public Health. 2023 May 25;11:1221666. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1221666. PMID: 37089476 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
[Etiology, diagnostics and classification of lunate bone necrosis].Unfallchirurg. 2018 May;121(5):373-380. doi: 10.1007/s00113-018-0495-6. Unfallchirurg. 2018. PMID: 29644422 Review. German.
-
Imaging of radial wrist pain. Part II: pathology.Skeletal Radiol. 2014 Jun;43(6):725-43. doi: 10.1007/s00256-014-1826-5. Epub 2014 Feb 14. Skeletal Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24522772 Review.
References
-
- Dumontier C. [Kienböck's disease. current data] Ann Radiol (Paris) 1992;35(5):373–383. - PubMed
-
- Decision No 1295/1999/Ec Of The European Parliament And Of The Council Of 29 April 1999 Adopting A Programme Of Community Action On Rare Diseases Within The Framework For Action In The Field Of Public Health (1999 to 2003)
-
- Wette A. Die Lunatumnekrose als Unfallfolge und Berufskrankheit. Arch Orthop Unfall- Chir. 1931;29:299–319. doi: 10.1007/BF02561908. - DOI
-
- Kaulbars U, Christ E, Dupuis H. Wirkung Von Greif- Und Andruckkraft Unter Schwingungsbelastung. Forschungsbericht Hand-Arm-Schwingungen III. Sankt Augustin: Hauptverband Der Gewerblichen Berufsgenossenschaften (HVBG); 1992.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

