Siglec-6 expression is increased in placentas from pregnancies complicated by preterm preeclampsia
- PMID: 23171684
- PMCID: PMC3676189
- DOI: 10.1177/1933719112461185
Siglec-6 expression is increased in placentas from pregnancies complicated by preterm preeclampsia
Abstract
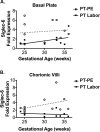
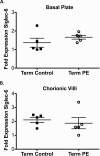
Sialic acid immunoglobulin-like lectin (Siglec)-6 is a transmembrane receptor that binds sialyl-TN glycans and leptin. Among eutherian mammals, only human placentas express Siglec-6. Previous work has implicated Siglec-6 in preeclampsia (PE). Preeclampsia, a leading cause of maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality, is characterized by placental abnormalities. This study provides a comprehensive analysis of Siglec-6 protein expression during human pregnancy by disease state (PE), biologic compartment (basal plate, chorionic villi, or maternal plasma), gestational age (24-41 weeks), and labor status. Siglec-6 protein was increased in both the basal plate and chorionic villi of preterm PE placentas (P < .05). However, expression did not differ at term by disease state, compartment, or labor status. Siglec-6 was not detectable in maternal serum. Overexpression of Siglec-6 protein in preterm PE placentas may contribute to or represent a response to PE pathogenesis and suggests that preterm PE pathogenesis is distinct from term PE.
Keywords: leptin; placenta; preeclampsia; siglec.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Glycosylated Siglec-6 expression in syncytiotrophoblast-derived extracellular vesicles from preeclampsia placentas.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Dec 17;533(4):838-844. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.09.081. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32998819
-
Upregulation of Siglec-6 induces mitochondrial dysfunction by promoting GPR20 expression in early-onset preeclampsia.J Transl Med. 2024 Jul 22;22(1):674. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05505-z. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39039496 Free PMC article.
-
Siglec-6 Signaling Uses Src Kinase Tyrosine Phosphorylation and SHP-2 Recruitment.Cells. 2022 Oct 29;11(21):3427. doi: 10.3390/cells11213427. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36359823 Free PMC article.
-
Severe preeclampsia-related changes in gene expression at the maternal-fetal interface include sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin-6 and pappalysin-2.Endocrinology. 2009 Jan;150(1):452-62. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-0990. Epub 2008 Sep 25. Endocrinology. 2009. PMID: 18818296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of B Cells in PE Pathophysiology: A Potential Target for Perinatal Cell-Based Therapy?Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 26;22(7):3405. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073405. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33810280 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Generating pregnant patient biological profiles by deconvoluting clinical records with electronic health record foundation models.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Sep 23;25(6):bbae574. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae574. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39545787 Free PMC article.
-
Siglec-9 is an inhibitory receptor on human mast cells in vitro.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023 Sep;152(3):711-724.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.04.007. Epub 2023 Apr 24. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37100120 Free PMC article.
-
The association between circulating SIGLEC6 and preeclampsia: observational studies of seven cohorts.EBioMedicine. 2025 Aug;118:105870. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105870. Epub 2025 Jul 29. EBioMedicine. 2025. PMID: 40737757 Free PMC article.
-
Differentially expressed genes in the pre-eclamptic placenta: a systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 12;8(7):e68991. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068991. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23874842 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of N-linked glycosylation and glycan-binding proteins in placentation: trophoblast infiltration, immunomodulation, angiogenesis, and pathophysiology.Biochem Soc Trans. 2023 Apr 26;51(2):639-653. doi: 10.1042/BST20221406. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023. PMID: 36929183 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Patel N, Brinkman-Van der Linden EC, Altmann SW, et al. OB-BP1/Siglec-6. a leptin- and sialic acid-binding protein of the immunoglobulin superfamily. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(32):22729–22738. - PubMed
-
- Brinkman-Van der Linden EC, Hurtado-Ziola N, Hayakawa T, et al. Human-specific expression of Siglec-6 in the placenta. Glycobiology. 2007;17(9):922–931. - PubMed
-
- Takei Y, Sasaki S, Fujiwara T, Takahashi E, Muto T, Nakamura Y. Molecular cloning of a novel gene similar to myeloid antigen CD33 and its specific expression in placenta. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1997;78(3-4):295–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

